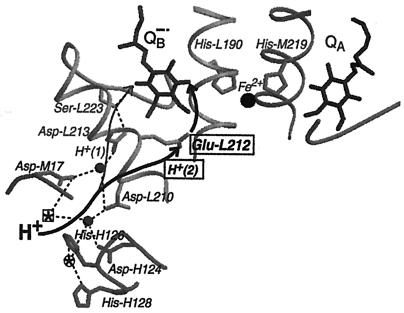
Figure 4.
Part of the structure of the RC from R. sphaeroides in the charge-separated state (coordinates are from ref. 5). Shown are the two quinones with their bridging amino acid residues, His-M219 and His-L190, and the nonheme Fe2+. The amino acid residues Asp-M17, Asp-L210, Asp-L213, Ser-L223, and Glu-L212, involved in proton transfer to QB are shown, with the transfer of H+(2) (bold) to Glu-L212 (boxed). The pathway (thin arrow) for H+(1) has recently been determined (8) and the pathway for H+(2) (bold arrow) was studied in this work. H+(2) is taken up to Glu-L212 in response to reduction of the quinones and then is transferred to QB after kAB(2) (see text and Fig. 1). Filled circles represent water molecules, and dashed lines potential hydrogen bonds. Also shown are Asp-H124, His-H126, and His-H128 that bind Zn2+ and Cd2+ at the circled star. Ni2+ binds to His-H126 and Asp-M17 at the boxed star (26). In the absence of metal ions, the positions of the circled and boxed stars are occupied by water molecules. The illustration was made by using the programs molscript (36) and raster3d (37).