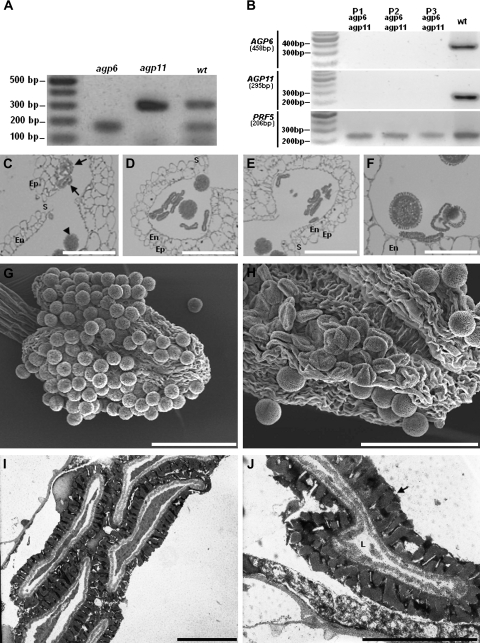
Fig. 2.
Ds transposon tag lines for AGP6 and AGP11. (A) Duplex RT-PCR amplification products of AGP6 and AGP11 mRNA transcripts in pollen of Arabidopsis wild-type (wt), and of Arabidopsis tag lines containing the Ds transposon in AGP6 (agp6) and in AGP11 (agp11) genes. Only in wild-type plants are the two expected amplification products visible. (B) RT-PCR amplification products of AGP6 and AGP11 mRNA transcripts in pollen of wild-type Arabidopsis (wt), and of three agp6 agp11 double mutant plants (P1, P2, P3). Figures under AGP and reference gene names refer to expected sizes of PCR amplification products. (C) Light micrograph of an anther of F1 plants, heterozygous for AGP6 and AGP11. Pollen grains show a collapsing phenotype (arrows) that contrasts with the ones that are roughly spherical pollen grains, and show no phenotype (arrow head). (D) Light micrograph of an anther of an agp6 F2 plant (and heterozygous for AGP11). At the time of dehiscence, more than 50% of the pollen grains show a collapsed phenotype. (E) Light micrograph of an anther of an agp11 F2 plant (and heterozygous for AGP6), exhibiting the same pollen morphology shown in (D). (F) Light micrograph of an anther of an agp6 agp11 double mutant F3 plant. Collapsing of pollen grains is evident, while some pollen grains still show a normal morphology. (G) Scanning electron micrograph of a wild-type dehiscent anther, showing normal roundish pollen grains. (H) Scanning electron micrograph of an agp6 agp11 double mutant dehiscent anther. The collapsed pollen grains are evident. (I) Transmission electron micrograph of an agp6 agp11 double mutant. The collapse of the pollen grain is evident. (J) High magnification transmission electron micrograph of pollen grains from of an agp6 agp11 double mutant. The pollen grain in the image shows a reduced cell lumen and a well-developed exine wall (arrow). En, endothecium; Ep, epidermis; L, cell lumen; S, stomium. Bars: (C, D, E, F) 20 μm; (G, H) 60 μm; (I, J) 5 μm.