Figure 6.
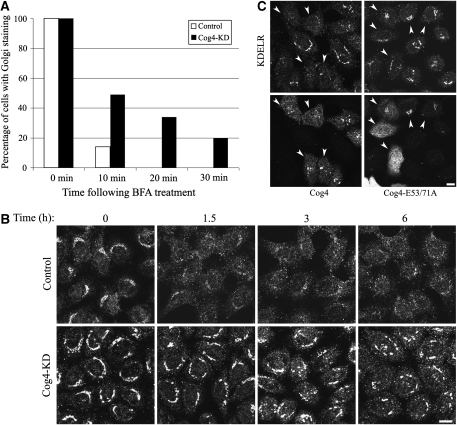
Cog4 restores Golgi-to-ER retrograde transport in a Sly1-interaction-dependent manner. (A) Depletion of Cog4 attenuates the transport of mannosidase II from the Golgi to the ER in response to BFA treatment. Control and Cog4-depleted HeLa cells were treated with BFA (5 μg/ml) for the indicated times, fixed, immunostained with anti-mannosidase II antibody, and analysed by confocal microscopy. The percentage of cells in which mannosidase II was localized to the Golgi was calculated from 200 cells at each time point. Representative confocal images are shown in Supplementary Figure S5A. (B) Depletion of Cog4 attenuates retrograde transport of KDELR. Control and Cog4-depleted HeLa cells were incubated at 15°C for the indicated times, to block protein exit from the ERGIC. The cells were then fixed, immunostained with anti-KDELR antibody and analysed by confocal microscopy. Shown are representative confocal images of control and Cog4-depleted cells at the indicated time points. Scale bar, 10 μm. (C) Cog4-depleted HeLa cells were transiently transfected with either the wild-type or E53/71A double mutant of Myc-tagged Cog4 containing the silent mutations within the RNAi targeting sequence. Two days later, the cells were incubated for 1.5 h at 15°C, fixed and double-immunostained with anti-Myc and anti-KDELR antibodies. Transfected cells are indicated by arrowheads. As shown, the wild-type Cog4, but not the E53/71A double mutant, restored retrograde transport of KDELR. Scale bar, 10 μm.