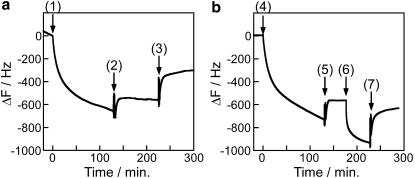
Figure 6.
Testing the reversibility of kinesin head and tail binding. (a) To test kinesin tail binding, 3.7 nM headless kinesin was washed onto a casein-pretreated SiO2 surface in the presence of 0.2 mg/mL casein (point 1). Note that because the solution preceding point 1 contained 0.2 mg/mL casein, the frequency change is caused solely by headless kinesin binding. At point 2, the solution was replaced with kinesin-free buffer containing 0.2 mg/mL casein to remove any unbound headless kinesin. At point 3, the solution was replaced with casein-free buffer to test whether casein dissociation resulted in kinesin dissociation. (b) To test kinesin head binding, 3.7 nM tailless kinesin was washed onto a casein-pretreated surface in casein-free buffer (point 4). At point 5, motor-free buffer was washed in, and at point 6, 0.2 mg/mL casein solution was washed in in an attempt to displace the bound motors. At point 7, solution was replaced by casein-free buffer to remove any motors that had been displaced by the soluble casein.