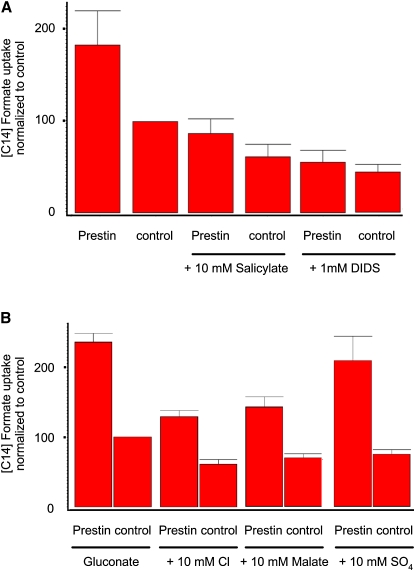
Figure 2.
Prestin-induced uptake of [14C]formate can be blocked. (A) [14C]formate uptake in cells transfected with prestin and vector only, and similarly transfected cells treated with 10 mM salicylate and 1 mM DIDS in incubation/preincubation medium. Prestin-induced uptake of [14C]formate was reduced by both agents. Mean values for the six groups were: prestin, 183 (±37); control, 100, prestin with salicylate, 87 (±16); control with salicylate, 61 (±13.0); prestin with DIDS, 53.9 (± 13.0); and control with DIDS, 44 (±8.5) (n = 3). (B) Effects of various test anions on prestin-induced uptake of [14C]formate. Prestin-transfected cells were incubated with Na gluconate and Na gluconate to which various indicated test anions were then added. Both chloride and malate decreased prestin uptake, whereas SO42− had minimal effects on prestin-induced [14C]formate uptake. Mean values for the eight groups were: prestin, 237 (±11.8); control, 100; prestin + chloride, 130 (±8.6); control + chloride, 61 (±6.7); prestin + malate, 142 (±15); control + malate, 70 (±5.7); prestin + SO42−, 209 (±35); and control + SO42−, 75 (±6.5). Uptake of [14C]formate by prestin was significantly reduced by chloride and malate (p < 0.05, one-way ANOVA), but not by SO42− (p > 0.05) (n = 3). Data were normalized to vector-only controls. Uptake is denoted in relative counts (see Methods).