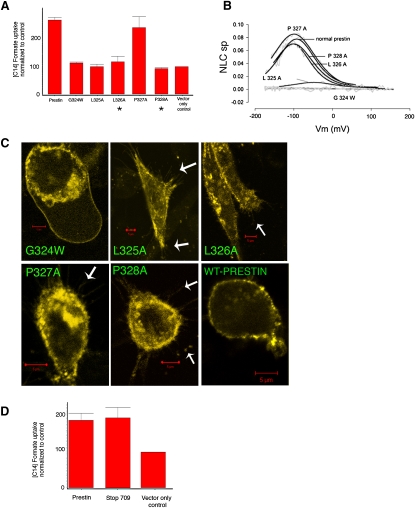
Figure 3.
Effects of truncations and mutations in prestin on prestin-induced uptake of [14C]formate. (A) Single mutations in potential chloride-binding motif decrease anion transport. All mutants except P327A show decreased anion transport. Mean uptake of [14C]formate of prestin, G324W, L325A, L326A, P327A, P328A, and vector-only control cells were 269 (±9), 113 (±3), 100 (±9), 117 (±20), 241 (±40), 93 (±3.5), and 100, respectively. The uptake of [14C]formate by prestin and P327A-transfected cells was significantly greater than in controls (p < 0.05, one-way ANOVA) (n = 4). (B) Effects of these mutations on NLC. Two mutants P328A and L326A show preserved NLC but decreased anion transport (indicated by asterisk in A). P327A has preserved NLC and anion transport, whereas remaining mutants eliminated (G324W) or significantly decreased (L325A) NLC, while also decreasing anion transport. (C) Confocal microscopy of YFP fusions of prestin and individual mutants (G324W, L325A, L326A, P327A, and P328A) shows membrane targeting. Arrows indicate filopodia containing prestin-YFP fluorescence. (D) Truncation of C-terminus at amino acid 709 (stop 709) that eliminates NLC shows preserved anion transport. Mean [14C]formate uptake values for prestin, stop 709, and vector-only control were 188 (±18), 197 (±28), and 100, respectively. The [14C]formate uptakes in prestin and stop 709-transfected cells were significantly greater than in controls (p < 0.05) (n = 3). Uptake is denoted in relative counts (see Methods).