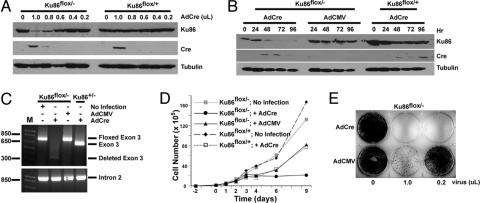
Fig. 2.
Characterization of a human Ku86 conditionally null cell line. (A) Documentation of the loss of Ku86 protein. Cell lines were exposed to the indicated dose of AdCre, and 3 days later whole-cell extracts were prepared and analyzed by Western blot analyses using antibodies directed against Ku86, Cre, and tubulin. A single blot is shown that was sequentially probed, stripped, and reprobed. (B) Same as A except that a time course rather than a dose–response is shown. AdCMV is a control, empty vector. (C) Molecular evidence for the loss of the floxed exon 3. The indicated cell lines were exposed to no virus, AdCMV, or AdCre virus. Genomic DNA was isolated 5 days later and subjected to PCR using primers that flank exon 3. A control PCR was performed by using a primer set located within intron 2. Both sets of PCR reactions were electrophoresed on agarose gels and stained with ethidium bromide. (D) Ku86flox/− cells exposed to Cre stop growing. The indicated cell lines were plated out 2 days before infection (day 0). The growth of the cells was monitored by counting live (trypan blue-excluding) cells at subsequent days. (E) Ku86flox/− cells exposed to Cre recombinase die. Ku86flox/− cells were exposed to the indicated amounts of either AdCre or AdCMV virus and then fixed and stained with crystal violet ≈14 days later.