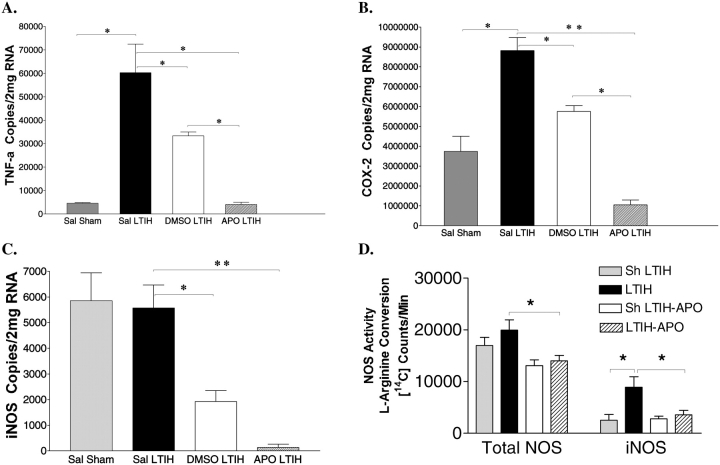
Figure 4.
NADPH oxidase inhibition confers resistance to the long-term intermittent hypoxia (LTIH) proinflammatory response. Proinflammatory gene expression was measured in micropunches in the lateral basal forebrains in gp91phox WT control mice (n = 10) and gp91phox-null mice (n = 10) for the following: (A) tumor necrosis factor α (TNF-α), (B) cyclooxygenase 2 (COX-2), and (C) inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) mRNA copies/2 μg total RNA. (D) Total NOS activity (left columns), measured as L-arginine conversion of [14C]L-arginine to L-citrulline, and iNOS activity (right columns) were measured using 5 mm S-ethyl-N-[4-trifluoromethyl)phenyl]isothiourea added to homogenates. Apocynin prevents the anticipated LTIH increase in iNOS activity. APO = apocynin in dimethylsulfoxide (DMSO) vehicle; sal = saline; sham = sham intermittent hypoxia control. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01.