Fig. 4.
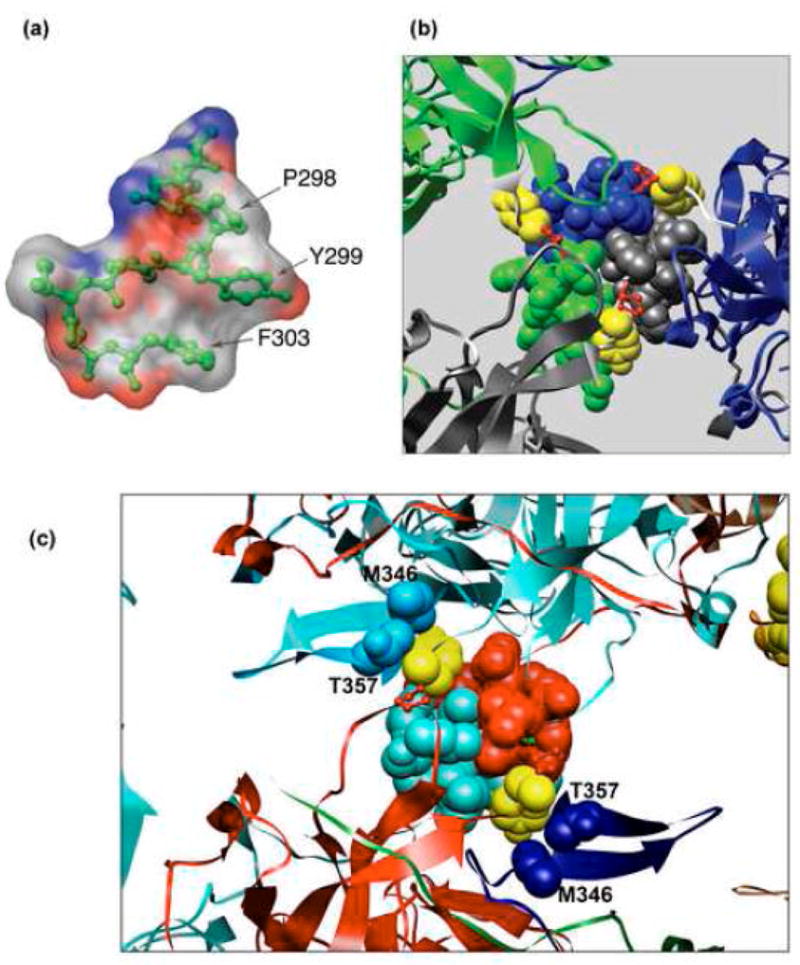
Interactions of Y299. (a). Stacking interactions within the α monomer involving Y299 stacked between P298 and F303. The surface is coloured according to CPK (Grey – carbon, blue – nitrogen, red – oxygen atoms). (b). Y299 covers the hydrophobic patch formed by the three C-terminal α helices. Representation of the hydrophobic interaction interface between VP1 monomer α (grey) α′ (blue) and α″ (green) tying the pentavalent pentamer (grey) with its neighbouring hexavalent pentamers. The three C-terminal α helices are represented as spheres. The monomer core is represented as ribbon. The hinge is shown in white, Y299 in yellow, and P300 in red. (c) Y299 interaction with distal part of the C-arm. The helices of monomers β (red) and β′ (turquoise) form two-fold, tight hydrophobic contacts between hexavalent pentamers. Y299 (yellow spheres) of these monomers interact with M346 and T357 (blue and light-blue spheres) which arrive from distant monomers in other pentamers, contributing to the interpentameric interaction. All Figures were created using CHIMERA.32
