Abstract
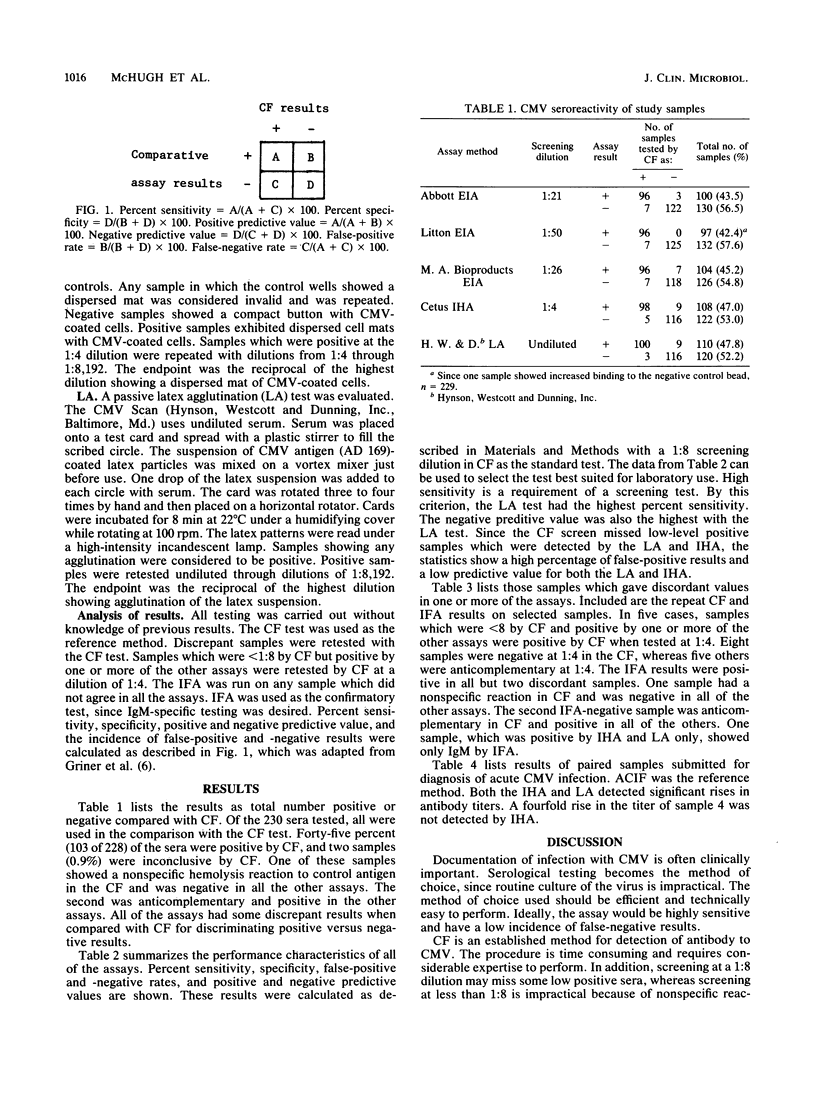
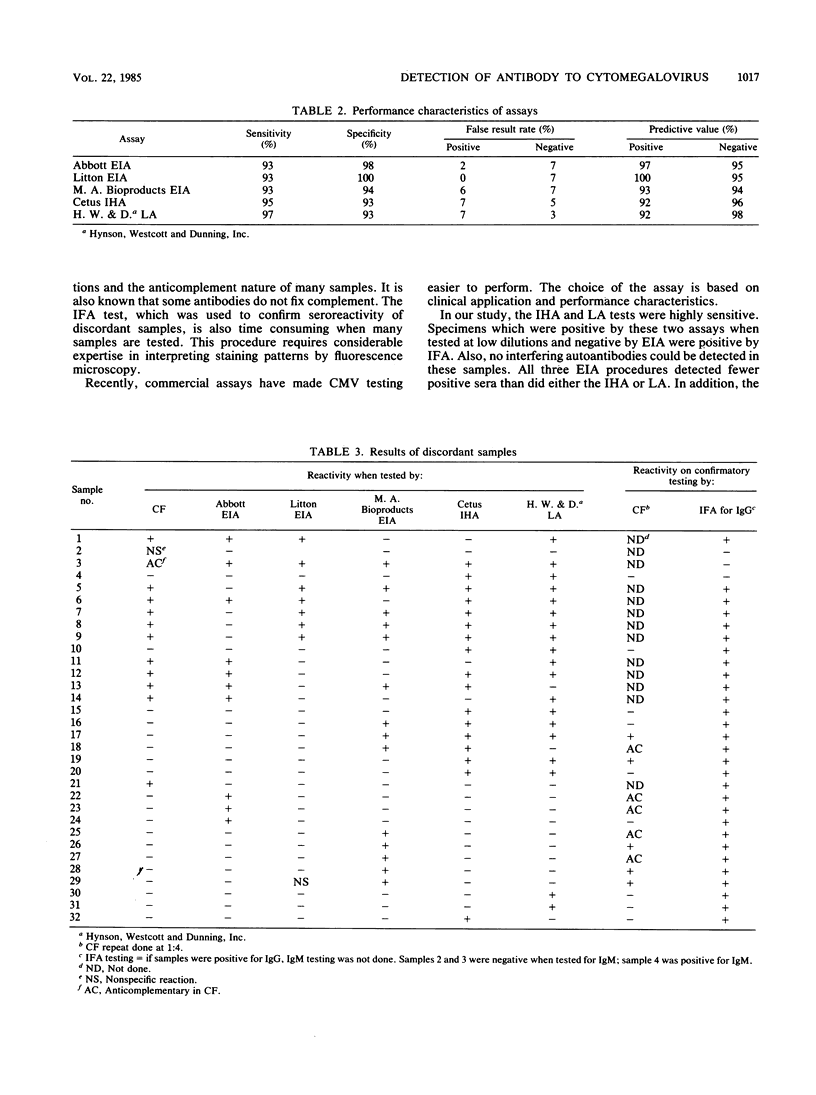
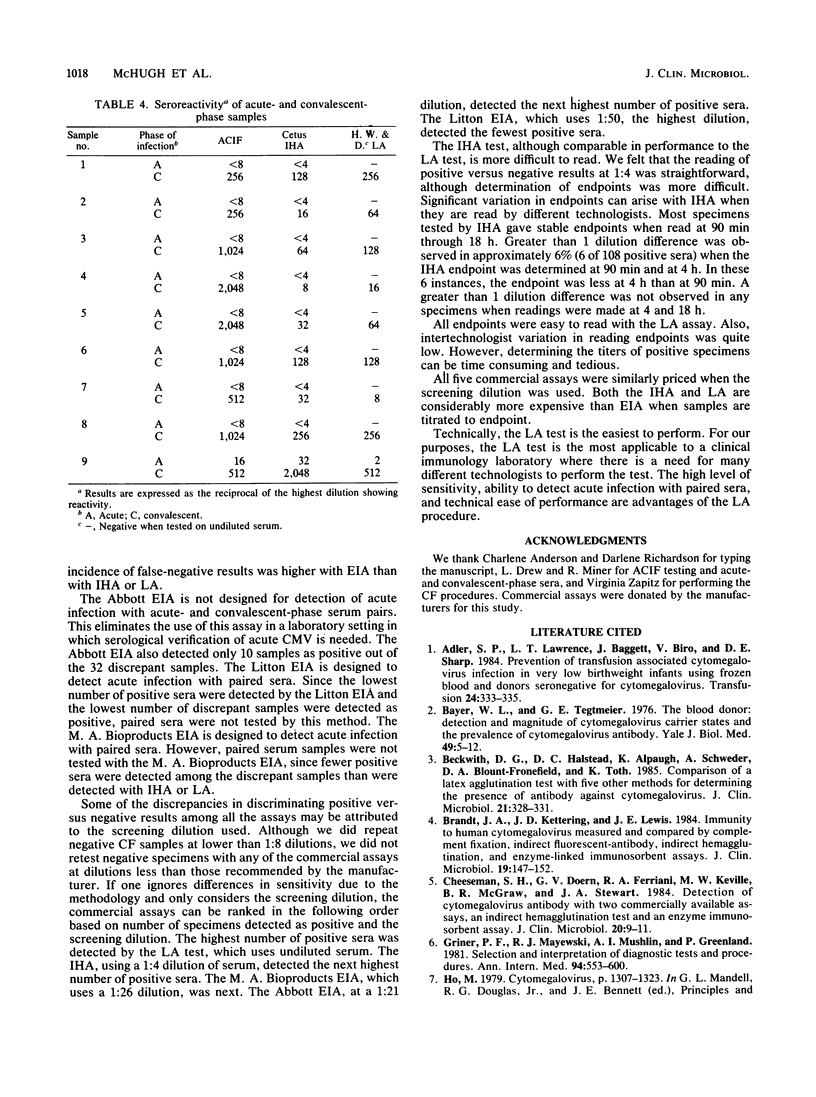
Five commercial assays were compared to a standardized complement fixation (CF) test for the detection of antibody to cytomegalovirus. Two hundred and thirty serum specimens were analyzed. In addition, nine pairs of acute- and convalescent-phase sera were tested by two of the commercial assays. The assays were compared as to sensitivity, specificity, and positive and negative predictive value, as well as incidence of false-positive and -negative results. Samples which did not agree in all the assays were retested and tested with an indirect fluorescent-antibody assay. Of 228 specimens, 103 (45.2%) were positive by CF. Of the 230 samples, 2 (0.9%) were inconclusive by CF and readable in the other assays. Of the 230 specimens, 97 (42.2%) were positive by an enzyme immunoassay (EIA; Litton Bionetics), 100 (43.5%) were positive by a second EIA (Abbott Laboratories), 104 (45.2%) were positive by a third EIA (M. A. Bioproducts). One hundred and eight (47.0%) were positive by indirect hemagglutination (IHA; Cetus Corporation), and 110 (47.8%) were positive by latex agglutination (LA; Hynson, Westcott and Dunning). Sensitivity and specificity were similar with all the assays (93 to 100%). The greater numbers of positive results by IHA and LA were confirmed by repeat CF testing at less than 1:8 dilution, and by indirect fluorescent-antibody assay. Acute- and convalescent-phase serum pairs showed a significant rise in antibody titer when tested by anticomplement immunofluorescence, IHA, and LA. There was good agreement among the assays, with LA having the highest sensitivity.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adler S. P., Lawrence L. T., Baggett J., Biro V., Sharp D. E. Prevention of transfusion-associated cytomegalovirus infection in very low-birthweight infants using frozen blood and donors seronegative for cytomegalovirus. Transfusion. 1984 Jul-Aug;24(4):333–335. doi: 10.1046/j.1537-2995.1984.24484275576.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bayer W. L., Tegtmeier G. E. The blood donor: detection and magnitude of cytomegalovirus carrier states and the prevalence of cytomegalovirus antibody. Yale J Biol Med. 1976 Mar;49(1):5–12. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beckwith D. G., Halstead D. C., Alpaugh K., Schweder A., Blount-Fronefield D. A., Toth K. Comparison of a latex agglutination test with five other methods for determining the presence of antibody against cytomegalovirus. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Mar;21(3):328–331. doi: 10.1128/jcm.21.3.328-331.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandt J. A., Kettering J. D., Lewis J. E. Immunity to human cytomegalovirus measured and compared by complement fixation, indirect fluorescent-antibody, indirect hemagglutination, and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Feb;19(2):147–152. doi: 10.1128/jcm.19.2.147-152.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheeseman S. H., Doern G. V., Ferriani R. A., Keville M. W., McGraw B. R., Stewart J. A. Detection of cytomegalovirus antibody with two commercially available assays, an indirect hemagglutination test and an enzyme immunosorbent assay. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Jul;20(1):9–11. doi: 10.1128/jcm.20.1.9-11.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunt A. F., Allen D. L., Brown R. L., Robb B. A., Puckett A. Y., Entwistle C. C. Comparative trial of six methods for the detection of CMV antibody in blood donors. J Clin Pathol. 1984 Jan;37(1):95–97. doi: 10.1136/jcp.37.1.95. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kangro H. O., Booth J. C., Bakir T. M., Tryhorn Y., Sutherland S. Detection of IgM antibodies against cytomegalovirus: comparison of two radioimmunoassays, enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay and immunofluorescent antibody test. J Med Virol. 1984;14(1):73–80. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890140111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luby J. P., Ware A. J., Hull A. R., Helderman J. H., Gailiunas P., Butler S., Atkins C. Disease due to cytomegalovirus and its long-term consequences in renal transplant recipients. Correlation of allograft survival with disease due to cytomegalovirus and rubella antibody level. Arch Intern Med. 1983 Jun;143(6):1126–1129. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mintz L., Miner R. C., Yeager A. S. Anticomplement immunofluorescence test that uses isolated fibroblast nuclei for detection of antibodies to human cytomegalovirus. J Clin Microbiol. 1980 Oct;12(4):562–565. doi: 10.1128/jcm.12.4.562-565.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monif G. R., Daicoff G. I., Flory L. L. Blood as a potential vehicle for the cytomegaloviruses. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1976 Oct 15;126(4):445–448. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(76)90636-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nankervis G. A. Cytomegalovirus infections in the blood recipient. Yale J Biol Med. 1976 Mar;49(1):13–15. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pagano J. S. Infections with cytomegalovirus in bone marrow transplantation: report of a workshop. J Infect Dis. 1975 Jul;132(1):114–120. doi: 10.1093/infdis/132.1.114. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phipps P. H., Grégoire L., Rossier E., Perry E. Comparison of five methods of cytomegalovirus antibody screening of blood donors. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Dec;18(6):1296–1300. doi: 10.1128/jcm.18.6.1296-1300.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rytel M. W., Balay J. Cytomegalovirus infection and immunity in renal allograft recipients: assessment of the competence of humoral immunity. Infect Immun. 1976 Jun;13(6):1633–1637. doi: 10.1128/iai.13.6.1633-1637.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yeager A. S., Grumet F. C., Hafleigh E. B., Arvin A. M., Bradley J. S., Prober C. G. Prevention of transfusion-acquired cytomegalovirus infections in newborn infants. J Pediatr. 1981 Feb;98(2):281–287. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(81)80662-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


