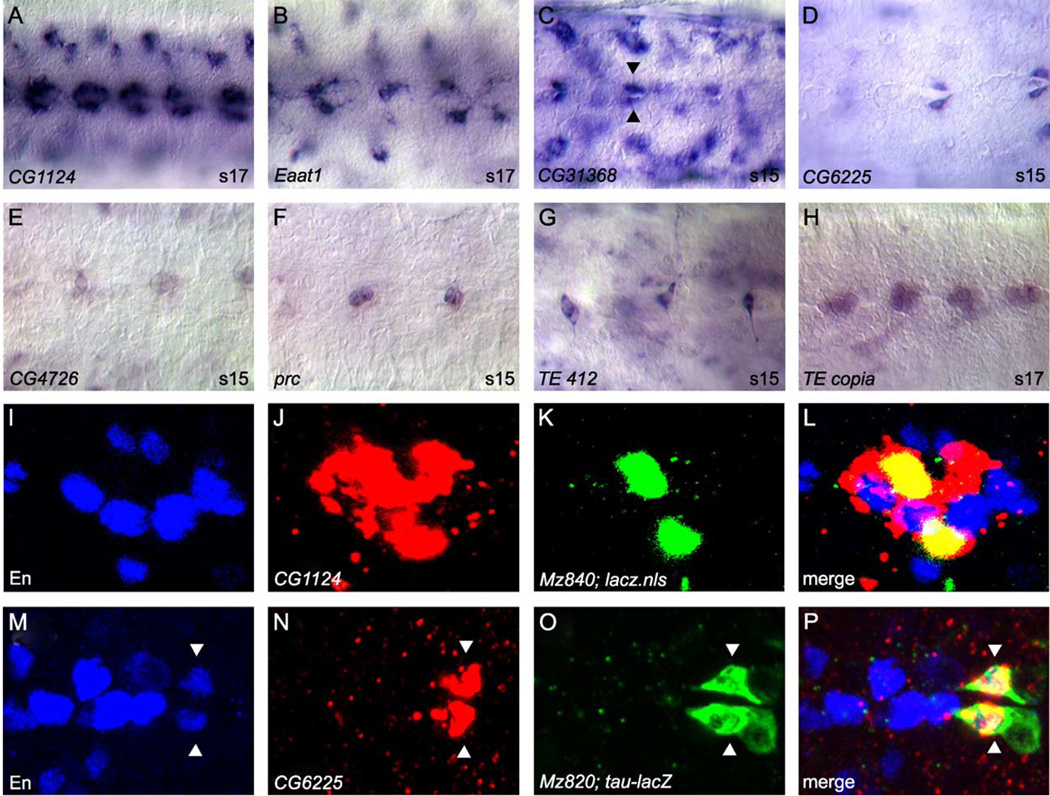
Fig. 6.
Midline accessory cell gene expression and midline-expressed transposable elements. (A–H) Whole-mount stage 15 or 17 embryos were hybridized to RNA probes and visualized by AP/DIC imaging. All views are ventral with anterior to the left. Magnification is 80x. (A–G) Examples of genes expressed in subsets of midline accessory cells, including (A–B) MM-CBG, (C–D) channel glia (arrowheads), and (E–G) DM cells. (G–H) Transposable element expression in midline and accessory cells, including (G) DM cells and (H) ventral neurons. (I–P) Confocal images of multi-label fluorescent in situ hybridization. An individual ganglion is shown for each panel. All views are ventral with anterior to the left. (I–L) Stage 16 Mz840-Gal4 × UAS-GFP-lacZ.nls embryo co-labeled with: (I) anti-En, (J) CG1124 RNA probe, and (K) anti-β-gal. (L, merge image) CG1124 expression (red) colocalizes with Mz840- driven nuclear β-gal (green) expression in MM-CBG. MM-CBGs are positioned just lateral to En-positive VUM cells. The in situ fluorescence stains the cytoplasm and is usually broader than the nuclear staining observed with immunostaining of GFP-lacZ.nls or nuclear proteins. (M–P) Stage 15 Mz820-Gal4 × UAS-tau-lacZ embryo co-labeled with: (M) anti-En, (N) CG6225 RNA probe, and (O) anti-β-gal. (P, merge image) CG6225 expression (red) co-localizes with tau-lacZ fusion protein (green) expressed in channel glia (arrowheads) via the Mz820-Gal4 enhancer trap line. CG6225-positive channel glia also express en.