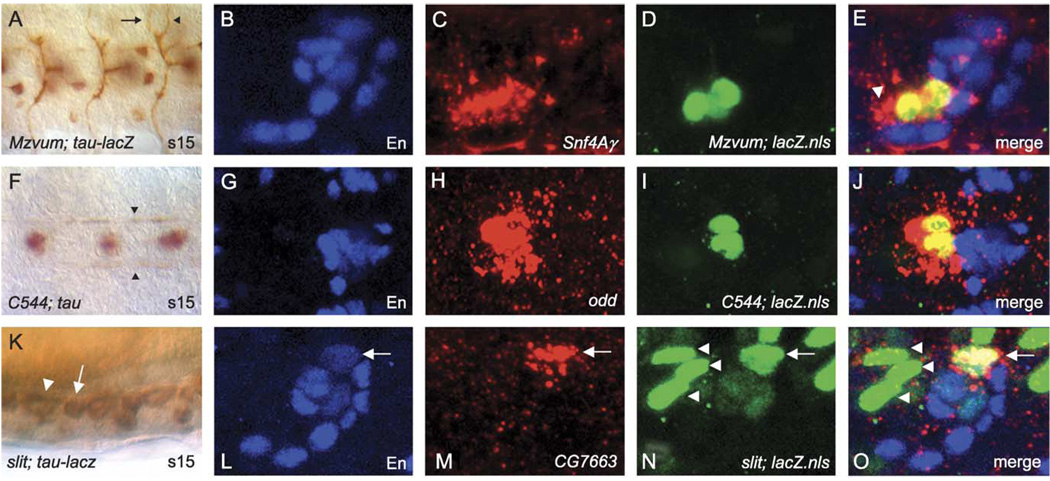
Fig. 7.
Cellular correspondence of midline gene expression. (A, F, K) DIC images of Gal4×UAS-tau or UAS-tau-lacZ embryos immunostained with anti-Tau or anti-β-gal. (B–E, G–J, L–O) Confocal images showing midline cell co-localization of RNA probes with defined midline cell markers. Anterior is to the left in all cases, and for sagittal views, dorsal is up. (A) Ventral view of stage 15 MzVUM-Gal4×UAS-tau-lacZ embryo showing the VUM motorneuron axonal trajectories that project out the intersegmental (arrow) and segmental (arrowhead) nerve roots. The VUM motorneuron cell bodies are out of the plane of focus. (B–E) Sagittal view of an individual ganglion from a MzVUM-Gal4×UAS-GFP-lacZ.nls embryo stained for (B) anti-En (blue), (C) Snf4Ay RNA (red), (D) anti-β-gal (green), and (E) merge image showing that Snf4Ay RNA co-localizes with β-gal-stained VUM motorneurons. Additional expression is detected just anterior to VUM motorneurons (arrowhead) and may represent staining in MP3 neurons. (F) Ventral view of a stage 15 C544-Gal4×UAS-tau embryo stained with anti-Tau showing the MP1 axonal trajectories along the longitudinal connectives (arrowheads). (G–J) Ventral view of an individual ganglion from a stage 16 C544-Gal4×UAS-GFP-lacZ.nls embryo stained for (G) anti-En (blue), (H) odd RNA (red), (I) anti-β-gal (green), and (J) merge image showing that odd RNA co-localizes with β-gal-stained MP1 neurons. (K) Sagittal view of stage 15 slit-gal4×UAS-tau-lacZ embryo showing anterior (arrowhead) and posterior (arrow) glia within a single ganglion. (L–O) Sagittal view of a single ganglion from a slit-Gal4×UAS-GFP-lacZ.nls embryo stained for (L) anti-En (blue), (M) CG7663 RNA (red), (N) anti-β-gal (green), and (O) merge image showing that CG7663 RNA co-localizes with β-gal and En-stained posterior glia (arrow). Posterior glia (arrow) can be easily distinguished from the three anterior glia (arrowheads) based on their relative positions along the A–P axis.