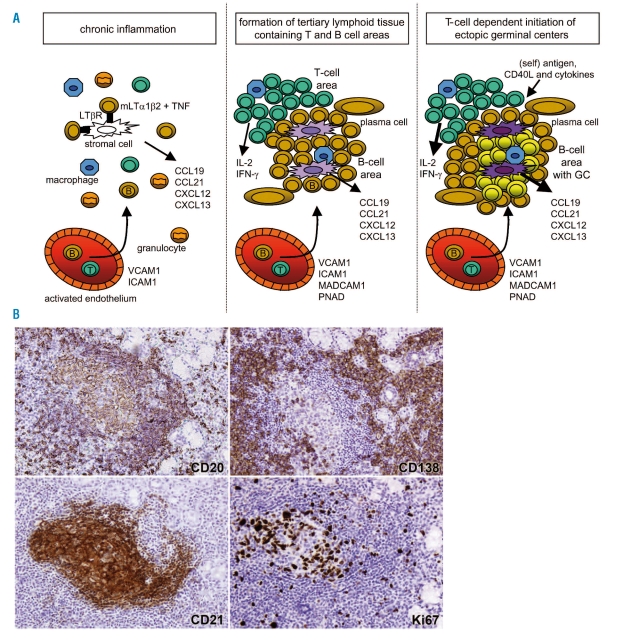
Figure 1.
Lymphoid tissue neogenesis and ectopic germinal center formation. Upper panels: (A) chronic inflammation is characterized by high levels of TNF, inducing stromal cells to produce CCL19 and CCL21 which attract B- and T- lymphocytes. (B) the interplay between CXCL13-producing stromal cells and increasing numbers of mLTα1β2 and TNF-expressing B lymphocytes, leads to the development of follicular dendritic cells (FDCs) and subsequent formation of lymphoid follicles. (c) T cells provide specific help to antigen activated B cells via costimulatory cytokines and membrane receptors. Lower panels: immunohistochemical stainings on a well-organized lymphoid infiltrate in a minor salivary gland of a Sjögren’s syndrome patient. Highlighted is a B-cell follicle including a germinal center using Abs specific for B cells CD20, plasma cells CD138, predominantly follicular dendritic cells CD21 and the proliferation marker Ki67.