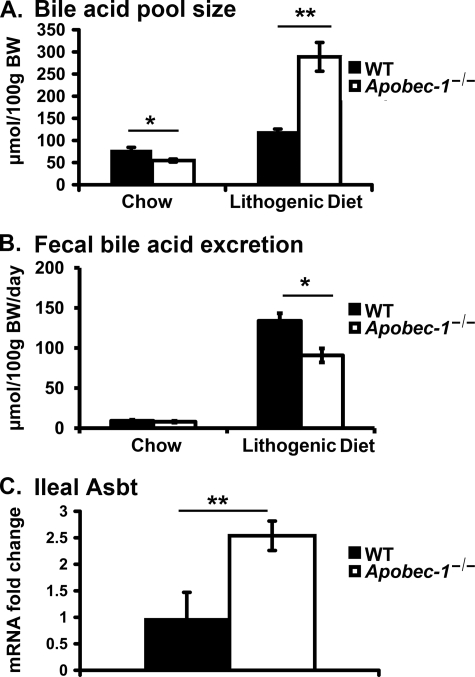
FIGURE 4.
Bile acid pool size, fecal bile acid excretion, and ileal Asbt (apical sodium-dependent bile acid transporter) mRNA expression. A, bile acid pool size (μmol/100 g of body weight) was decreased in Apobec-1−/− mice on a chow diet but increased in Apobec-1−/− mice fed an LD for 2 weeks. Liver, gallbladder, and intestine were pooled and subjected to ethanolic bile acid extraction. Total bile acid mass was measured enzymatically. B, fecal bile acid excretion was comparable in chow-fed mice of both genotypes, but LD-fed Apobec-1−/− mice excrete less bile acid than WT controls. Mice were individually housed, and feces were collected up to 72 h. Fecal bile acids were extracted and quantitated enzymatically. C, Asbt mRNA abundance is increased in LD-fed Apobec-1−/− mice. RNA was extracted from ileum of LD-fed WT and Apobec-1−/− mice, and Asbt expression was measured by qRT-PCR. Bar graphs represent the mean ± S.E. from 5 mice/genotype on chow and 4 mice/genotype on LD. *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01.