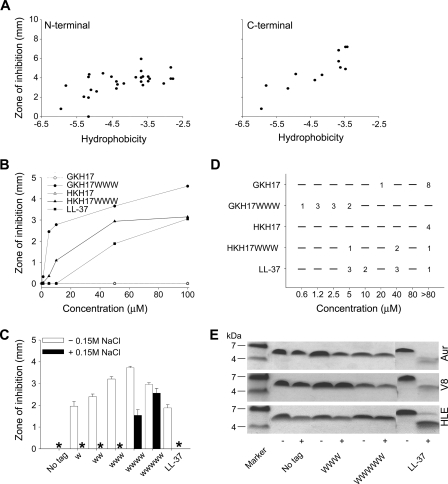
FIGURE 1.
Antibacterial activities and protease effects of peptides. A, antimicrobial activity as assessed by RDA against S. aureus of peptides with either N-terminal (left panel) or C-terminal (right panel) hydrophobic modifications. For determination of activity, bacteria (4 × 106 CFU/ml) were inoculated in 0.1% TSB-agarose gel, and 4-mm wells were punched. In each well, 6 μl of peptide (at 100 μm) was loaded. The zones of clearance correspond to the inhibitory effect of each peptide after incubation at 37 °C for 18–24 h (mean values, n = 3). The activity is plotted versus peptide hydrophobicity (Kyte and Doolittle scale). (The correlation coefficient (R) and the coefficient of determination (R2) in Fig. 1A are 0.583 and 0.340, respectively, for the N-terminal modifications, and 0.881 and 0.776, respectively, for the C-terminal modifications.) B, dose-dependent activity of the selected peptides GKH17 and HKH17 and WWW-tagged variants against S. aureus (4 × 106 CFU) in RDA. (The difference between the original peptides GKH17, HKH17, and their tagged variants is significant (p < 0.05, two-way ANOVA).) C, effect of tag length on GKH17 peptide activity (at 50 μm) against S. aureus ATCC 29213 as assessed by RDA in the presence and absence of 0.15 m NaCl. * denotes no detectable clearance zone. (In absence of salt the difference between all tagged peptides, and no tag is significant. In presence of 0.15 m NaCl, the difference between the WWW and WWWWW peptides versus no tag is significant (p < 0.05, one-way ANOVA).) D, MIC of indicated peptides against different S. aureus isolates. E, protease sensitivity of peptides. The indicated peptides were incubated with (+) or without (−) the S. aureus enzymes aureolysin (Aur), V8 proteinase (V8), or human leukocyte elastase (HLE) and analyzed by SDS-PAGE (16.5% Tris-Tricine gels).