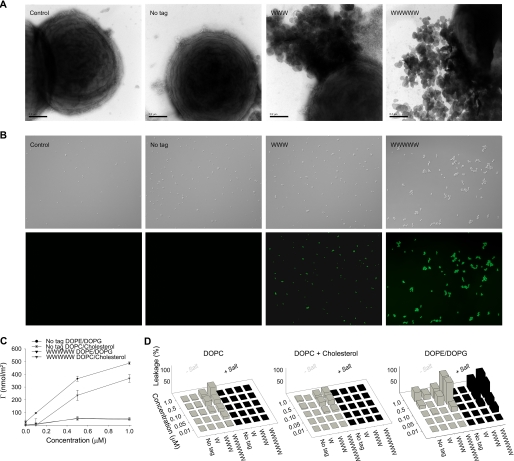
FIGURE 3.
Peptide-mediated permeabilization of S. aureus bacteria and liposomes. A, S. aureus ATCC 29213 was incubated with GKH17 and the indicated hydrophobically modified variants (all at 30 μm) and analyzed with electron microscopy (negative staining). The scale bars correspond to 0.5 μm. B, bacterial viability after incubation with peptides. S. aureus ATCC 29213 was incubated with GKH17 or Trp-tagged GKH17 peptides (all at 30 μm) in buffer at physiological salt (0.15 m NaCl) for 2 h at 37 °C. The upper images in each row are Nomarski Differential Interference Contrast images, whereas the lower images show fluorescein isothiocyanate fluorescence of bacteria. C, peptide adsorption to supported lipid bilayers composed of DOPC/cholesterol (60/40 mol/mol; zwitterionic) and DOPE/DOPG (75/25 mol/mol; anionic). (There is statistical difference between control GKH17 and GKH17-WWWWW, as well as between DOPE/DOPG and DOPC/cholesterol for GKH17-WWWWW (p < 0.05, Student's t test).) D, effects of peptides on liposomes in the presence and absence of 0.15 m NaCl. The membrane-permeabilizing effect was recorded by measuring fluorescence release of carboxyfluorescein from liposomes. The left panel shows DOPC (zwitterionic) liposomes, the center panel shows DOPC/cholesterol (60/40 mol/mol; zwitterionic) liposomes, and the right panel shows DOPE/DOPG (75/25 mol/mol; anionic) liposomes.