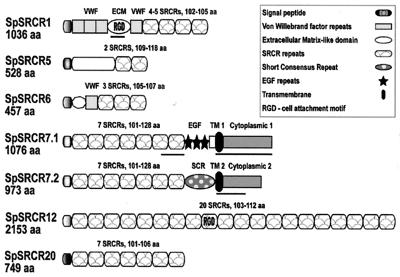
Figure 1.
Structure of six purple sea urchin coelomocyte SRCR proteins. Four of these SRCR molecules are mosaic, including vWF repeats in SpSRCR1 and SpSRCR6 (61–62 amino acids long) and another domain in SpSRCR1 (ECM, 347 amino acids), which is similar to an ECM protein of another sea urchin. SpSRCR7.1 features three epidermal growth factor (EGF) repeats (34–38 amino acids), whereas in SpSRCR7.2, there is one short consensus repeat (SCR) of the complement control superfamily (68 amino acids). In both SpSRCR7 variants, the N terminus is conserved (11-aa substitutions in residues 1–795), but immediately after the seventh SRCR, the predicted transmembrane domains, C terminus, and 3′ UTR regions are different. Other domains are not similar to any published sequences, such as the N-terminal domains in SpSRCR5 (amino acid 285) and SpSRCR6 (amino acid 53) and the domain that separates the EGF-like repeats from the membrane retention domain in SpSRCR7.1 (amino acid 52). Clones of SpSRCR1 differ in the number of SRCRs, displaying four or five domains within otherwise similar transcripts. Segments in SpSRCR1 and SpSRCR7 that were used as domain-specific probes are underlined: the ECM, the seventh SRCR, and cytoplasmic domains 1 and 2. Accession numbers for these sequences are SpSRCR1, AF076513; SpSRCR5, AF076514; SpSRCR6, AF228823; SpSRCR7.1, AF228824; SpSRCR7.2, AF228825; SpSRCR12, AF064259; and SpSRCR20, AF228826.