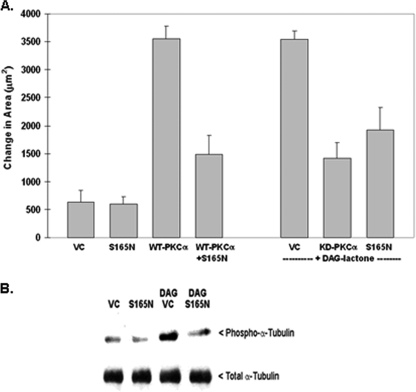
FIGURE 3.
Phosphorylation-resistant α6-tubulin mutant (S165N) inhibits motility of MCF-10A cells and decreases phosphorylation of endogenous α-tubulin. A, S165N-α6-tubulin suppresses motile behavior of stimulated MCF-10A cells. Following expression of the S165N mutant (GFP-(S165N)-α6-tubulin), cells were tested for a dominant negative effect on motility that had been induced by either WT PKCα overexpression or by treatment with 5 μm DAG-lactone for the duration of the experiment. The ability of the S165N mutant to impede motility was compared with that of the kinase-defective mutant of PKCα (KD). An equivalent amount of plasmid DNA (4 μg) was used for all transfections. B, S165N-α6-tubulin suppresses DAG-lactone-stimulated phosphorylation of endogenous α-tubulin in MCF-10A cells. Cells were transfected with 4 μg of S165N mutant or the VC. Identical transfectants were treated with 5 μm DAG-lactone or DMSO (0.1%, v/v) for 30 min at 37 °C prior to lysis. Lysates were prepared in 0.2 ml of microtubule stabilization-extraction buffer (0.1 m PIPES, pH 6.9, 30% glycerol, 5% DMSO, 1 mm MgSO4, 1 mm EGTA, and 1% Triton X-100) containing protease inhibitors and 10 μm BIM. A soluble fraction containing unincorporated tubulin was prepared from lysates (see “Materials and Methods”) and normalized for total protein content (280 μg), and each sample volume was adjusted to 1.0 ml with radioimmune precipitation buffer. The samples were precleared with mouse IgG-agarose and immunoprecipitated with 2 μg of mouse anti-α-tubulin for 15 h with rotation at 4 °C. Immunopellets were divided into duplicate blots and probed in parallel with either rabbit polyclonal phospho-PKC substrate antibody (1:500 dilution) or rabbit anti-α-tubulin (1:2500 dilution). The results are representative of three independent experiments.