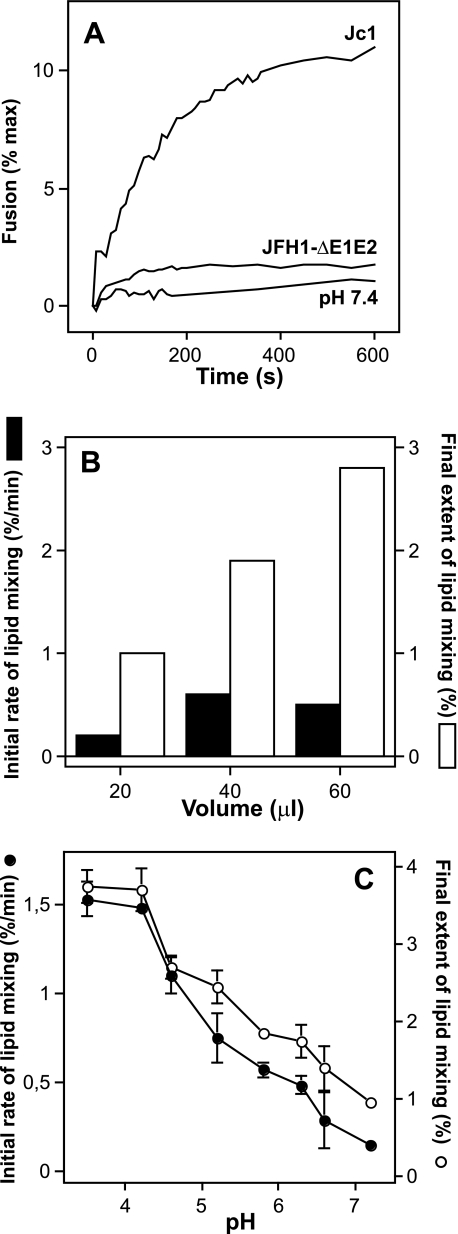
FIGURE 1.
Characteristics of HCVcc-Jc1 membrane fusion. A, representative experiment of Jc1-mediated lipid mixing (100 μl) with R18-labeled PC:chol liposomes (15 μm final concentration; see “Materials and Methods”). Culture fluid of Jc1- or JFH1-ΔE1E2-transfected Huh-7.5 cells was harvested 48 h post-transfection, concentrated (10-fold), and partially purified by ultracentrifugation through a 20% sucrose cushion. The respective pellets were resuspended in PBS and directly applied to the fusion assay. At time 0, fusion was initiated by acidifying the medium to pH 5.0 through addition of diluted HCl to the cuvette containing PBS. The value for complete lipid mixing, which corresponds to 100% fluorescence, was obtained by adding 0.1% (v/v, final) Triton X-100 to the suspension. B, representative experiment of the influence of viral dose on Jc1 fusion. Increasing amounts of Jc1 viruses (in μl) were added to the cuvette containing fluorescent liposomes in PBS, and lipid mixing was recorded at pH 5.0; solid bars, initial rate; open bars, final extent of lipid mixing. C, pH dependence of Jc1 lipid mixing. Lipid mixing was recorded at the indicated pH; initial rates were determined for each pH from the tangents to the steepest part of the fusion curves (closed symbols). The final extent of lipid mixing is the value of fluorescence for each pH at the 10-min time point (open symbols). Each point represents the average value of three separate measurements.