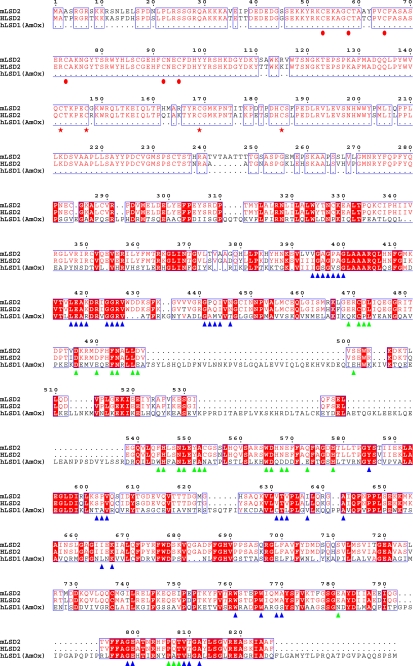
FIGURE 2.
Sequence alignment of LSD2 from M. musculus (mLSD2; NCBI gene identifier 26986558), LSD2 from Homo sapiens (hLSD2; gene identifier 122889312), and LSD1 from H. sapiens (hLSD1; gene identifier 58761545). With regard to human LSD1, only the region that has been used for crystallographic studies (residues 171–852) (19, 20) has been included in the alignment because the N-terminal segment of LSD1 is not homologous to that of LSD2 (see Fig. 1b). Residues conserved in mLSD2 and hLSD2 are indicated by the red font, whereas amino acids that are conserved among all three aligned proteins are highlighted in red. The triangles outline the amino acids involved in FAD (blue) and substrate binding (green), as gathered from the analysis of the human LSD1·CoREST crystal structures (19, 20). The red circles indicate the conserved N-terminal Cys residues, which might represent potential zinc-binding sites. The red stars outline the conserved cysteines of the predicted CW-type zinc finger domain (30). Residue numbering refers to mLSD2. Identity values for the aligned sequences are: 92% between mLSD2 and hLSD2; 32% between mLSD2 and hLSD1; and 33% between hLSD1 and hLSD2.