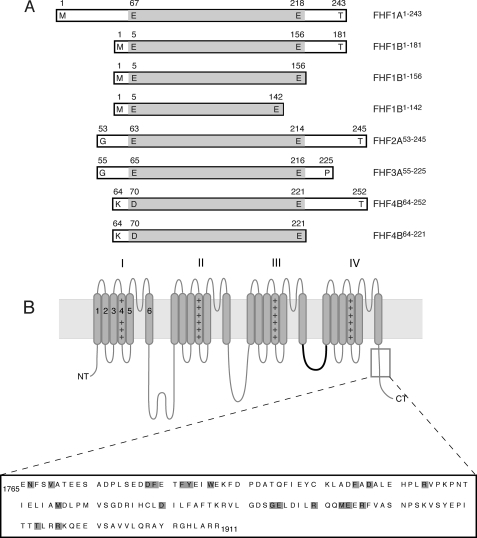
FIGURE 1.
Schematic of FHF and channel constructs used in this study. A, FHF constructs. Boundaries of each construct are labeled. The boundaries of the FHF homology core region are shaded gray. B, topology of the Nav α subunit. The four homologous domains of the α subunit (labeled I-IV), each containing six transmembrane α-helical segments (gray rods labeled 1–6) form the ion conduction pore. The fourth segment of each domain contains positive charge clusters (++) and is part of the voltage sensors. The intracellular loop linking domains III and IV functions as the fast inactivation gate (highlighted in bold). The C-terminal region, which binds FHFs, is boxed, and the primary sequence of this region in murine Nav1.6 (residues 1765–1911) is shown. The positions of pathogenic mutations in this channel region are shaded gray.