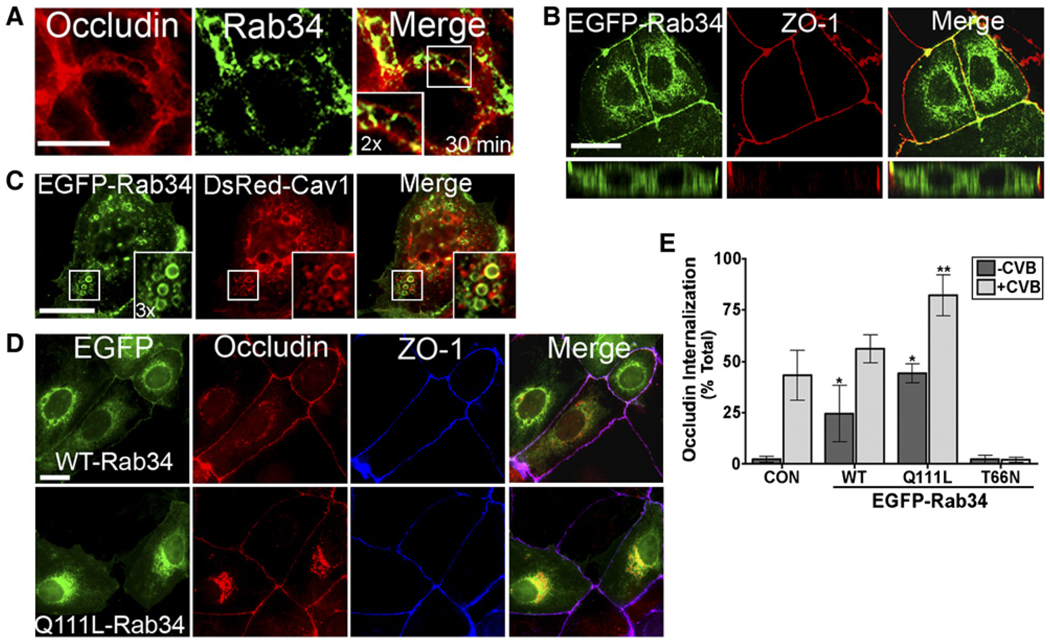
Figure 4. Rab34 Localizes to Tight Junctions and Mediates Occludin Internalization.
(A) Monolayers were exposed to CVB (100 PFU/cell) for 30 min at 37°C and then fixed and stained for occludin (red) and Rab34 (green).
(B) Cells expressing wild-type EGFP-Rab34 were fixed and stained for ZO-1 (red).
(C) Colocalization of EGFP-Rab34 and DsRed-caveolin-1. Insert, 33 zoomed image.
(D) Cells expressing wild-type (WT) or constitutively active (Q111L) EGFP-Rab34 were fixed and stained for occludin (red) and ZO-1 (blue).
(E) Quantification of occludin internalization in cells transfected with a GFP control plasmid (CON), or wild-type (WT), constitutively active (Q111L) EGFP-Rab34, dominant-negative (T66N) Rab34. Cells were either exposed to no virus (−CVB) or exposed to CVB (+CVB) for 90 min at 37°C. Data are representative of at least three independent experiments performed three times. Data in (E) are shown as mean ± standard deviation. *p < 0.05.