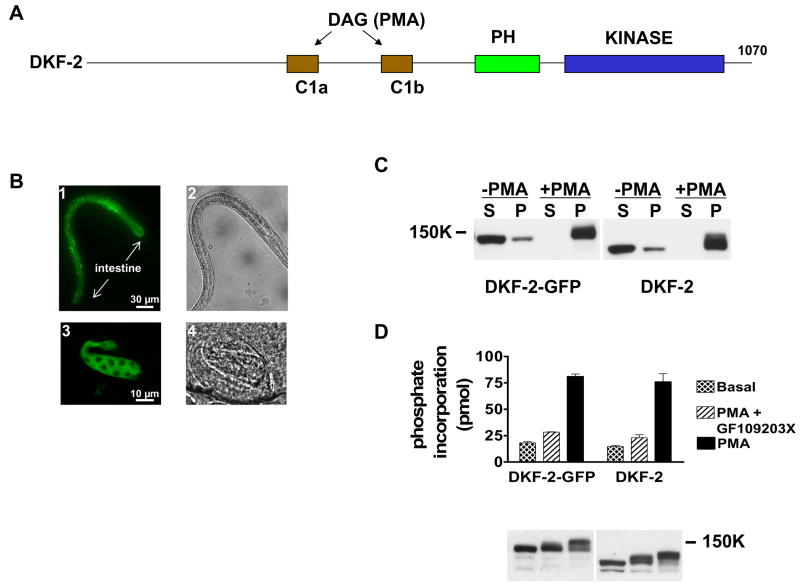
Figure 1. DKF-2-GFP Is Fully Functional and Selectively Expressed in Intestine.
A depicts locations of C1, PH and kinase domains along the DKF-2 polypeptide. B, animals expressing a dkf-2::DKF-2-GFP transgene were created. GFP-derived fluorescence was recorded using a Zeiss Axio Imager Z1 microscope and AxioVision software. Arrows mark anterior and posterior ends of the intestine. B1 (L2 larva) and B3 (late embryo) show DKF-2-GFP is dispersed in intestinal cells. B2 and B4 are Nomarski interference images of B1 and B3, respectively. C is a Western immunoblot containing cytosolic (S) and membrane (P) proteins (30 μg/lane) isolated from HEK293 cells expressing DKF-2-GFP (lanes 1–4) or DKF-2 (lanes 5–8). Cells were incubated with 0.3 μM PMA (10 min) as indicated. Cytosol and membranes were isolated as previously reported (Feng et al., 2007). The blot was probed with anti-DKF-2 IgGs and chemiluminescence signals were recorded on X-ray film. D, transfected cells expressing DKF-2-GFP or DKF-2 were treated with 0.3 μM PMA or vehicle (basal) for 10 min. Duplicate samples of cells were incubated with pan-PKC inhibitor GF109203X for 1 h prior to PMA addition. Cells were lysed, and DKF-2 proteins were immunoprecipitated and assayed for catalytic activity as described in Experimental Procedures. An immunoblot shows similar amounts of DKF-2 were used in each assay (D, lower panel). Increases in apparent Mr of DKF-2 in PMA-treated cells (C, D) are due to phosphorylation catalyzed by PKCs and other protein kinases.