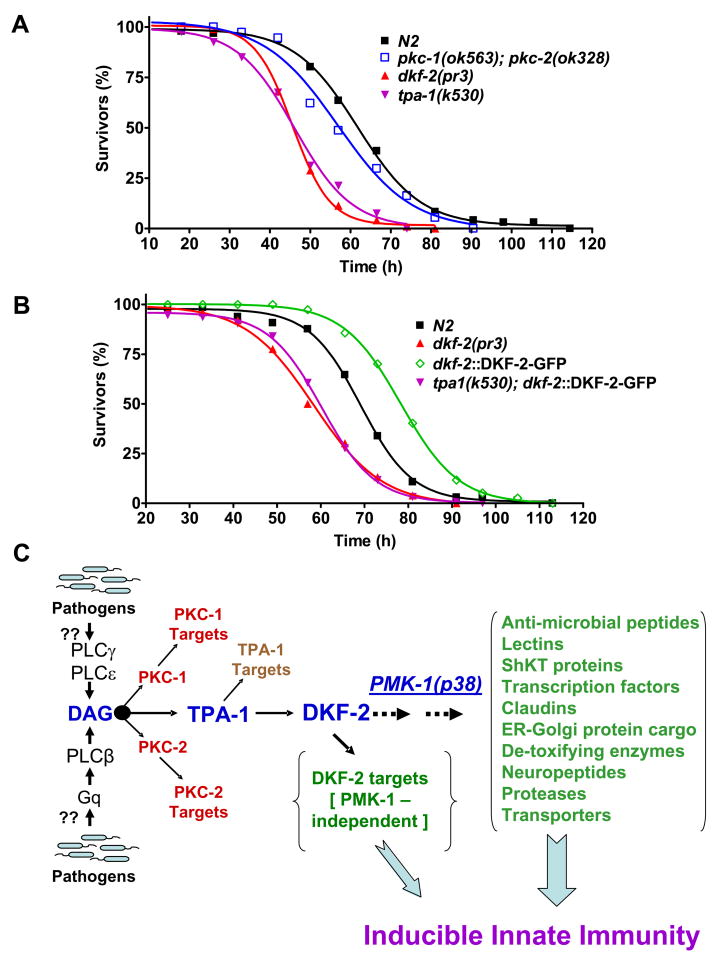
Figure 7. TPA-1 Controls DKF-2.
A depicts survival curves for dkf-2(pr3) null, pkc-1(ok563);pkc-2(ok328) double null and tpa-1(k530) defective C. elegans mutants feeding on PA14. B shows survival curves for WT, dkf-2(pr3) and transgenic (dkf-2::DKF-2-GFP and tpa-1(k530);dkf-2::DKF-2-GFP) nematodes fed PA14. C presents a model for (partial) regulation of immunity by a DAG→TPA-1→DKF-2 signaling pathway in C. elegans. We speculate that pathogens directly/indirectly activate PLCs, thereby increasing DAG levels. DAG recruits and activates TPA-1, which phosphorylates and activates DAG-bound DKF-2. DKF-2, a PKD prototype, induces expression of immune effector mRNAs that defend intestinal cells against pathogens via PMK-1 dependent and independent mechanisms.