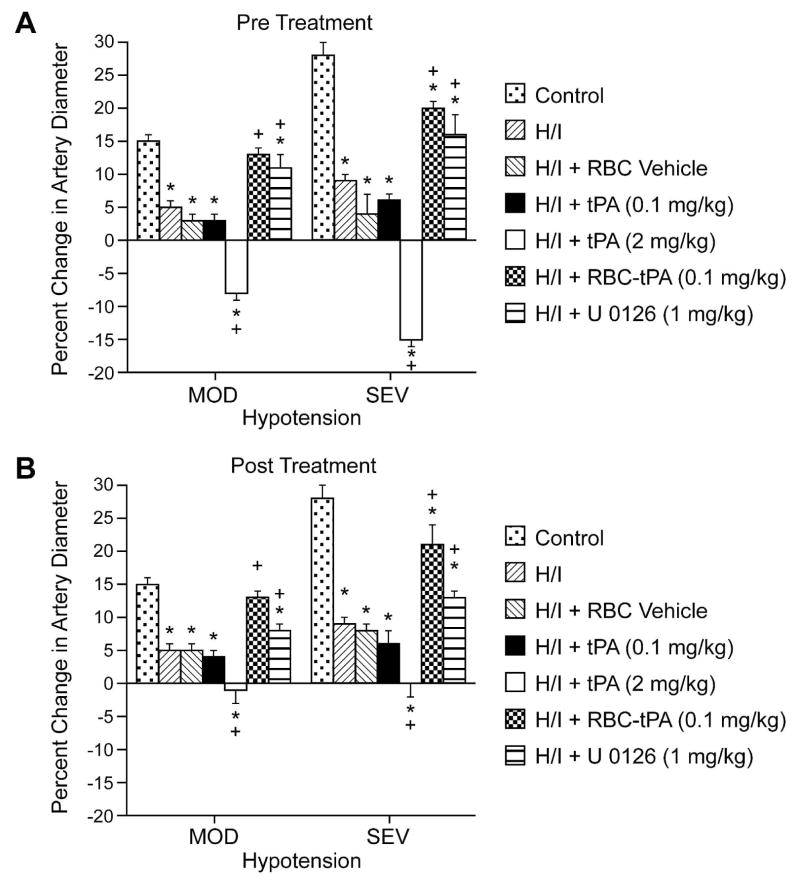
Figure 3.
Soluble tPA administration aggravates H/I induced impairment of hypotensive pial artery dilation, whereas RBC-tPA prevents hypotensive dilator impairment. Influence of hypotension (mod,sev; 25 and 45% reductions in mean arterial blood pressure for 10 min) on pial artery diameter before (control), 2.5h after hypoxia/ischemia (H/I), after H/I treated with RBC vehicle, after H/I treated with tPA (0.1 mg/kg iv), after H/I treated with tPA (2 mg/kg iv), after H/I treated with RBC-tPA (0.1mg/kg iv), and after H/I treated with U 0126 (1 mg/kg iv), n=4–6. A: pretreatment 30 before H/I B: post treatment 2h after H/I *P<0.05 versus corresponding control value +P<0.05 versus corresponding non treated H/I value.