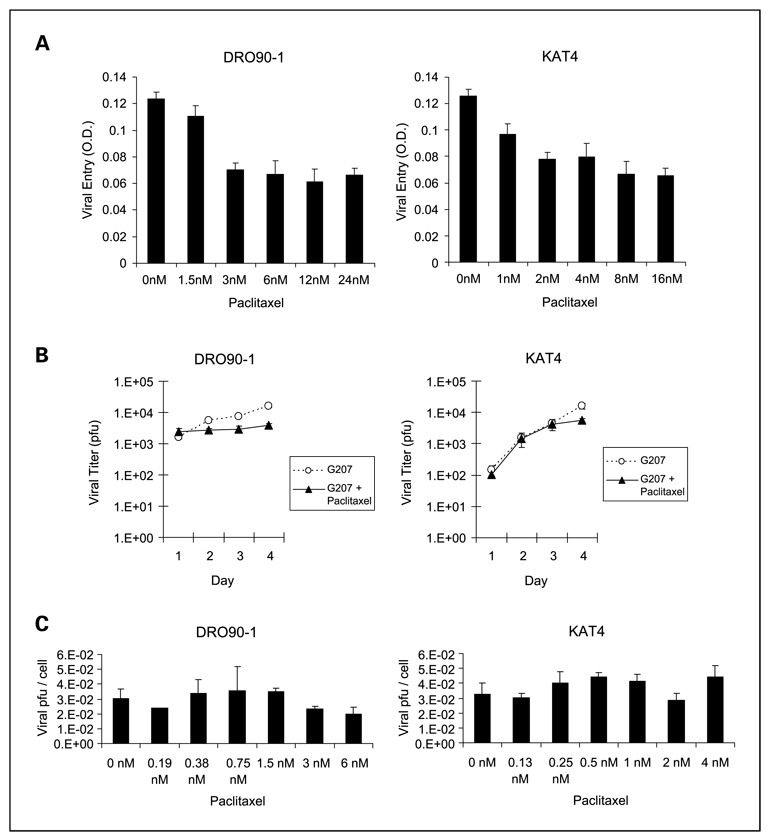
Fig. 3.
Paclitaxel fails to increase G207 viral entry or viral proliferation. A, measures of G207 viral entry and early gene expression assessed by lacZ assays in ATC cell lines show modest but significant decreases with low-dose paclitaxel and stable effects at doses higher than 2 nmol/L. B, total G207 viral proliferation per well was measured after exposure of ATC cells to G207 atMOI of 0.5 (KAT4) orMOI of 1.5 (DRO90-1) in combination with paclitaxel at 1nmol/L (KAT4) or 3 nmol/L (DRO90-1).Viral titers were calculated daily by plaque assays, and the number of recovered pfu was assessed. The combination of paclitaxel with G207 slightly impaired viral replication compared with G207 alone in DRO90-1cells and was not affected in KAT4 cells. C, G207 viral proliferation was measured in combination with a range of paclitaxel concentrations at 48 h after exposure to G207 atMOI of 1. Recovered viral pfu were adjusted per viable cell number to account for varying cytotoxic effects. There were no significant differences in the amount of recovered G207 per viable cell with or without the addition of paclitaxel at doses up to 6 nmol/L. Columns, mean; bars, SE.