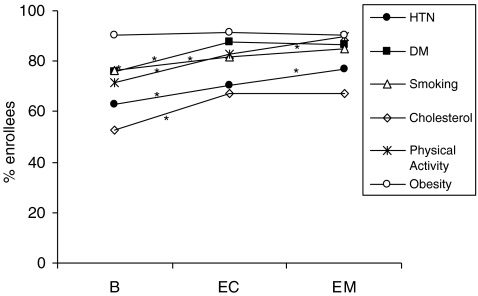
Fig. 4.
Effects of the intervention on knowledge of cardiovascular risk modification for participants who completed all assessments. Cardiovascular outcomes (proportion of women) at baseline (B), end of counseling (EC), and end of maintenance (EM) for women enrolled in the study. All comparisons are paired (pre- or post-intervention) for women with data at all three time points. Knowledge of effective cardiovascular risk modification interventions (e.g., utility of decreased sodium intake for blood pressure control, utility of decreased fat intake for control of high cholesterol, etc.) were assessed for each of the following risk factors: diabetes (DM), hypertension (HTN), high cholesterol, obesity, physical inactivity, and smoking. Statistically significant changes (*p < 0.05) for comparisons of B to EC and EC to EM are noted