Figure 4.
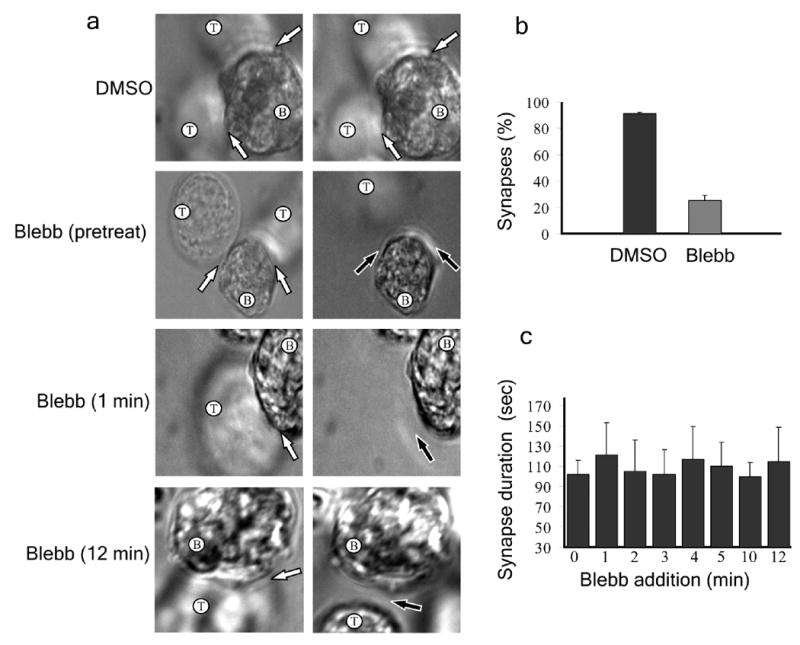
Effect of inhibiting myosin IIA activity on immunological synapse stability. (a) SEE superantigen-loaded B cells were immobilized in dishes with coverslip inserts and Jurkat T cells were added and allowed to form immunological synapses. T cells were either pretreated with DMSO or blebbistatin or were treated with blebbistatin following synapse formation at the indicated times. DIC images were taken before treatment (left) and between 1–2 min after treatment (right). T and B cells are indicated; immunological synapses are denoted by white arrows and loss of synapse is denoted by black arrow. (b) Percentage of synapses present 2 minutes after blebbistatin addition. (c) Average duration of conjugates when blebbistatin was added at various times after synapse formation. (b,c) n = 35. Error bars indicate standard deviation.
