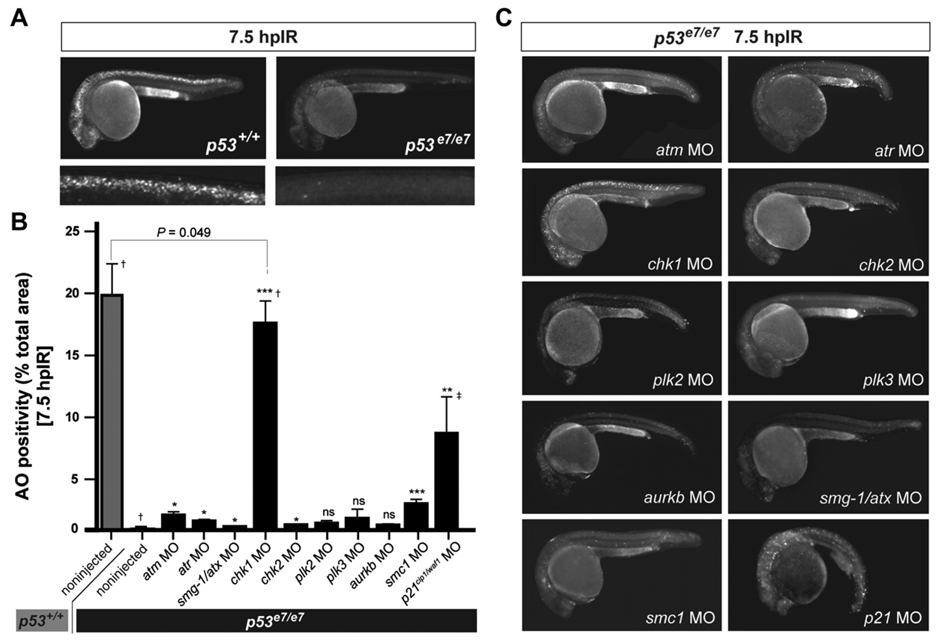
Figure 1. A Morpholino Screen Identifies chk1 as a Loss-of-Function Suppressor of p53e7/e7-Associated Radioresistance.
(A) Live 25 hpf embryos of the indicated genotypes stained with AO at 7.5 hpIR (12.5 Gy). Anterior, left. Note the complete absence of AO labeling in the brain and spinal cord of the irradiated p53 mutant.
(B) MO screen for loss-of-function suppressors of p53e7/e7-associated radioresistance. Noninjected and 1 cell-stage MO-injected embryos were irradiated at 18 hpf (12.5 Gy). AO uptake by cells was quantified by analyzing images of whole embryos photographed live at 7.5 hpIR (y axis) (images as in C). Injected MOs are indicated along the x axis. Bars are color coded and refer to the genetic background used for injections (gray, p53+/+; black, p53e7/e7). AO staining was quantified in ≥ 8 embryos per knockdown, with 50 or more embryos scored per knockdown (except †> 1000); ‡, embryos showed developmental defects. All data are reported as means ± SEM. Statistical significance versus the noninjected p53e7/e7 response: * p < 0.05; ** p < 0.005; *** p < 0.0005; ns (not significant), (two-tailed Student’s t test).
(C) Fluorescent images of AO-labeled, live p53 mutants injected with indicated MOs and representative of the phenotypes quantified in (B).