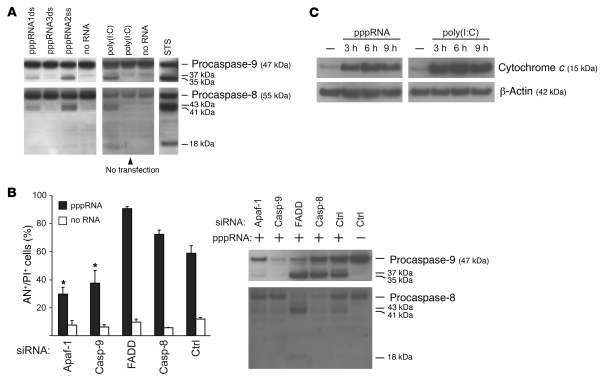
Figure 4. RIG-I and MDA-5 activate the mitochondrial apoptosis pathway.
(A) Transfection of pppRNA or poly(I:C) activates the initiator caspase-9 and -8. pppRNAs (pppRNA1–3) or poly(I:C) (5 ng/ml) were used with or without transfection reagent, and 1205Lu cells were analyzed 12 (pppRNA) or 24 hours [poly(I:C)] after RNA treatment. Caspase activation was assessed by immunoblotting with antibodies that are specific for both procaspases and their respective active subunits. WM9 melanoma cells treated with 1 μM staurosporine (STS) for 5 hours served as a positive control for caspase cleavage. Blots are representative of 3 independent experiments. The last lane of the upper-left blot was run on the same gel but was not contiguous, as indicated by the white line. (B) 1205Lu cells were treated with pppRNA or transfection reagent alone 48 hours after transfection of siRNAs specific for Apaf-1, caspase-9, FADD, caspase-8, or control siRNA. Left: Apoptotic and dead cells (AN+/PI+) were analyzed. Mean ± SD of 3 independent experiments is shown. *P ≤ 0.05 compared with control siRNA–transfected cells treated with pppRNA. Right: Analysis of caspase-8 and -9 activation 12 hours after pppRNA transfection by immunoblotting as described for A. Blots are representative of 2 independent experiments. (C) 1205Lu cells were treated with pppRNA or poly(I:C) (5 ng/ml) or left untreated. Cytosolic protein fractions were prepared at the indicated time points (3, 6, or 9 hours after transfection) and analyzed for the presence of cytochrome c in the cytosol by immunoblotting. β-Actin served as loading control. Blots are representative of 2 independent experiments.