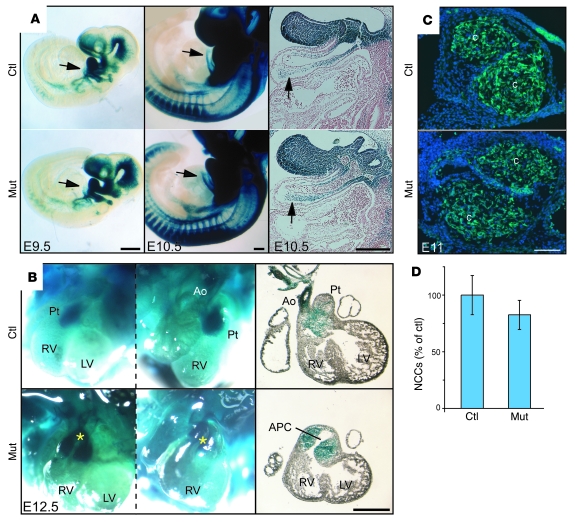
Figure 2. Normal neural crest migration in conditional Fak mutant embryos.
(A) Whole mounts of E9.5 and E10.5 X-gal–stained embryos. The right column shows sagittal sections of E10.5 embryos stained with Fast Red. Arrows indicate colonization of the outflow tract by cardiac NCCs (blue). (B) Whole mounts of E12.5 X-gal–stained hearts. Asterisks show positions of the great arteries in mutant embryos, showing misalignment of the great arteries and abnormal aorticopulmonary communication (APC). The left column shows frontal views; the middle column shows right views; the right column shows frontal histological sections of the hearts. (C) Frontal cryostat sections of E11 embryos at distal outflow tract levels. Cardiac NCCs (green) are able to colonize the outflow tract of mutants and form conotruncal cushions (c). (D) No significant difference was found in the number of NCCs in E11 control and mutant outflow tracts. This analysis was performed using 10 serial sections, 30 μm apart, with locations matched between control and mutant littermates. A minimal conotruncal cushion area of 0.22 mm2 was analyzed from each embryo. Data are expressed as mean ± SD. Scale bars: 250 μm (A); 500 μm (B); 100 μm (C).