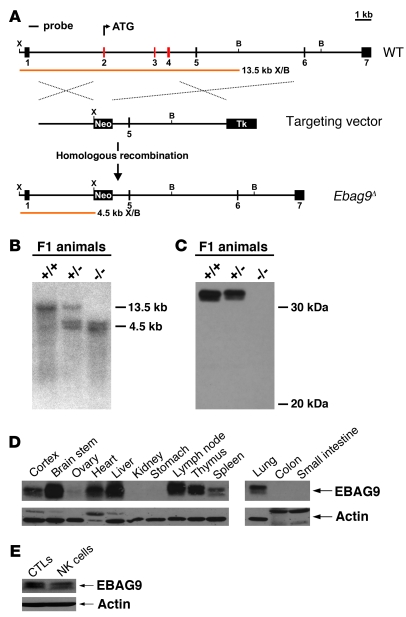
Figure 1. Generation of Ebag9 mutant mice.
(A) Schematic representation of the targeting strategy employed to disrupt the Ebag9 gene. The WT Ebag9 locus (top), the targeting vector (middle), and the mutated locus (Ebag9Δ) after homologous recombination (bottom) are shown. The Ebag9 gene consists of 7 exons; exons removed after homologous recombination are shown in red. The predicted fragment sizes after XhoI (X) and BamHI (B) digestion of genomic DNA are indicated. Neo, neomycin resistance cassette; Tk, thymidine kinase cassette. (B) Southern blot analysis of XhoI/BamHI-digested genomic DNA from F1 animals using the probe indicated in A. (C) Western blot analysis of EBAG9 expression in lymph nodes from adult mice, using polyclonal anti-EBAG9 serum. (D) Differential expression of the EBAG9 protein in various tissues analyzed by immunoblot. (E) Immunoblot analysis of EBAG9 expression in WT CTLs and NK cells.