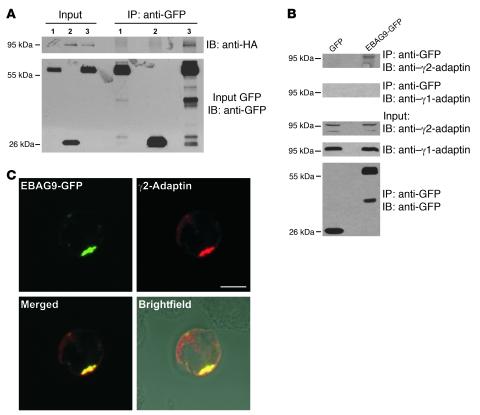
Figure 10. Coimmunoprecipitation of EBAG9 and γ2-adaptin in vivo.
(A) GFP or EBAG9-GFP stably expressing MDA cells were transiently transfected with γ2-adaptin–HA. Cells were solubilized in Triton X-100 lysis buffer and subjected to immunoprecipitation with anti-GFP mAb. Coimmunoprecipitated γ2-adaptin–HA was detected by immunoblotting with an anti-HA mAb. EBAG9-GFP and GFP were detected with biotinylated anti-GFP antibody (input GFP). Input was 1/100 volume of the reaction mixture. Lane 1, MDA-MB435-EBAG9-GFP; lane 2, MDA-MB435-GFP plus γ2-adaptin–HA; lane 3, MDA-MB435-EBAG9-GFP plus γ2-adaptin–HA. (B) Stably transfected MDA-MB435-EBAG9-GFP and GFP-transfected control cells (1 × 107) were solubilized in Triton X-100–containing lysis buffer and subjected to immunoprecipitation with anti-GFP mAb. Coimmunoprecipitated endogenous γ2-adaptin was detected in immunoblotting with a γ2-adaptin–specific antibody. EBAG9-GFP and GFP were detected with biotinylated anti-GFP antibody (input GFP). (C) Colocalization of EBAG9-GFP and γ2-adaptin in a perinuclear localization. Jurkat cells were cotransfected with EBAG9-GFP and γ2-adaptin–HA. Cells were fixed, permeabilized, and then stained with anti-HA mAb. Images were analyzed by confocal microscopy, and colocalization was assessed by calculating the Pearson’s correlation coefficient r of at least 30 cells analyzed in 2 independent experiments (mean r = 0.469). For EBAG9-GFP and anti-GM130, mean r = 0.63 (for EBAG9-GFP and anti-GFP, rmax = 0.95). Scale bar: 5 μm.