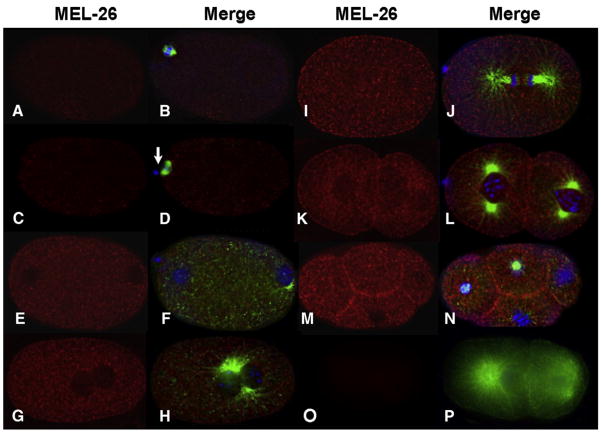
Fig. 1.
Time course of MEL-26 accumulation in wild-type embryos. The left column shows deconvolved indirect immunofluorescence images of embryos stained with anti-MEL-26 (red) while the right column shows merged images of the same embryos stained with anti-MEL-26 (red), anti-tubulin (green) and DAPI (blue). (A, B) meiosis I. (C, D) Meiosis II, note the first polar body (arrow). (E, F) Pronuclear formation, levels of MEL-26 have increased. (G, H) Pronuclear fusion. (I, J) Anaphase of the first mitotic division. (K, L) Late two cell stage, and (M, N) four cell stage. Note that MEL-26 is enriched at the membrane between cells of multicellular embryos. (O, P) Two cell mel-26(ct61sb4); tbb-2(sb26) shows no MEL-26 staining. The mutation encoded by the allele ct61sb4 results in a truncation N-terminal to the region used to raise the antisera. tbb-2(sb26) suppresses ct61sb4 lethality, restoring normal embryo morphology. Note that the low levels of MEL-26 present at meiosis I and II (A–D) are above the background seen in (O, P).