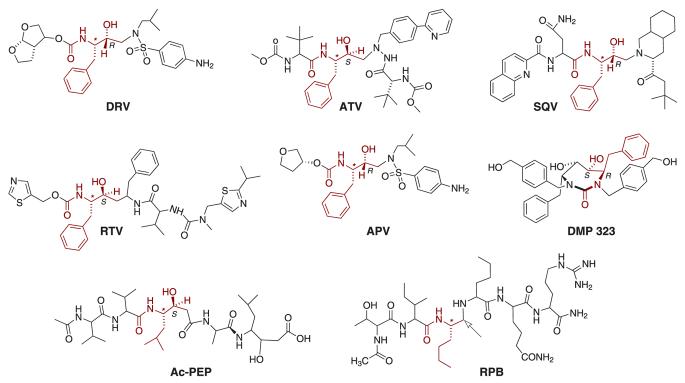
Fig. 1. Structures of the PR inhibitors.
The structures are oriented so that the motif corresponding to P1, that is common to all the clinical inhibitors, as well as analogous substructures in the other inhibitors, are overlaid. Absolute configurations (shown only for the two carbon atoms in this common motif) in the acyclic inhibitors are S for the carbon atoms marked with an asterisk, and otherwise are as indicated. Note that in RPB the hydroxymethylene moiety is replaced by a methylene group (reduced peptide bond) as shown by the arrow.