Figure 4.
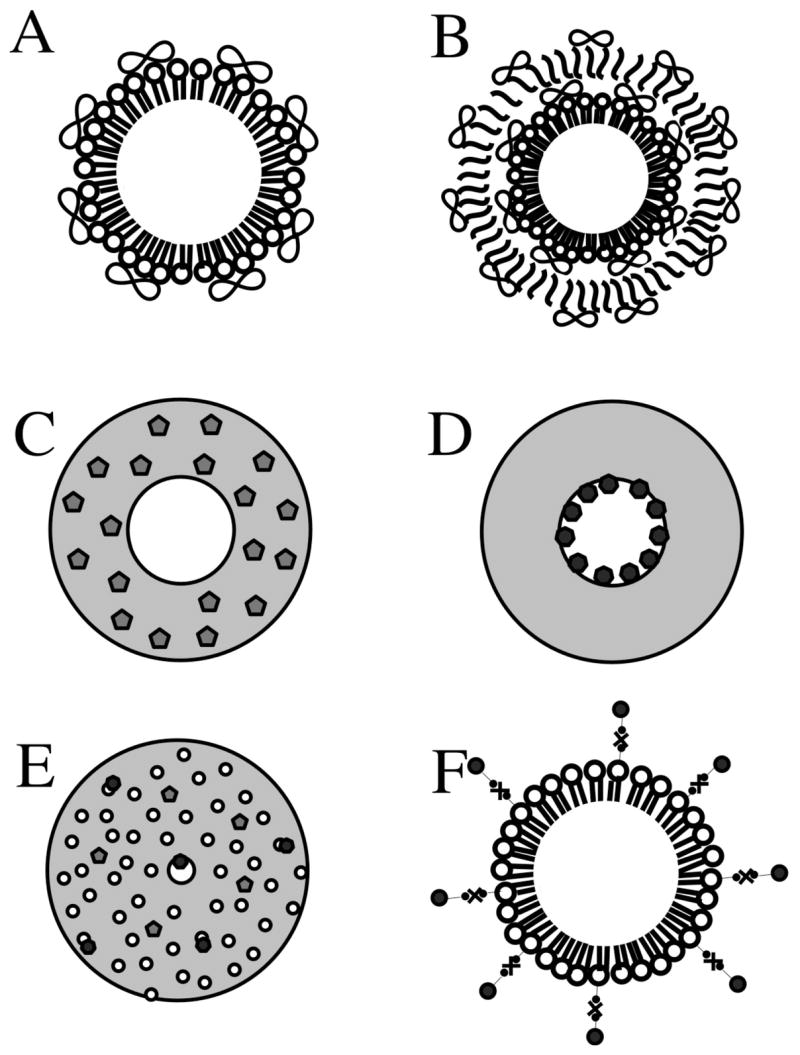
Schematic representation of loading strategies of drugs and genes on microbubbles. (A) Non-covalently binding of DNA to the surface of cationic lipid microbubbles. (B) Multilayered structure based on a lipid microbubble sequentially coated with DNA and poly-L-lysine layers. Polymeric microbubbles with central hollow core surrounded by a thick polymeric shell. (C) Polymeric microbubble loaded with hydrophobic drug loaded in the shell phase. (D) Polymeric microbubble with hydrophilic drug loaded in the internal void. (E) Internal structure of polymeric microbubbles: water-phase is dispersed through the polymer matrix, forming upon lyophilization a plurality of cavities distributed over the particle volume. (F) Attachment of liposomes or nanoparticles to the surface of microbubbles through biotin-avidin-biotin bridging system. The drawing is not to scale.
