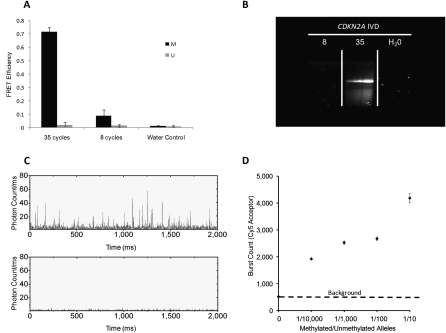
Figure 2.
High analytical sensitivity facilitated by inherent low-background noise. (A) Methylation for CDKN2A can be detected as early as eight cycles as demonstrated by the FRET efficiency, which is significantly higher than that of water control. FRET efficiency from the standard 35-cycle control is much higher due to both a stronger acceptor emission accompanied by stronger QD quenching. Error bars are computed from five separate experiments. (B) Corresponding MSP gel readout indicates no visible band at eight cycles for methylated CDKN2A product but a clear band for the standard 35 cycles. (C) Confocal spectroscopy is used to observe differences in the positive control (IVD only) and negative control (NL only) through 2000-msec single-particle traces. (Top) In positive control, each Cy5 peak seen is the fluorescence burst associated with labeled-MSP products that is linked to a single QD passing through the focal detection volume of a confocal spectroscopy setup. (Bottom) The negative control has very low background noise. (D) IVD was serially diluted in NL DNA (150 ng) and subject to MS-qFRET with 40 cycles of amplification. Confocal spectroscopy is used to analyze fluorescent bursts for the acceptor (Cy5) and was plotted for the entire time duration (three separate runs of 100 sec) for 1/10, 1/100, 1/1000, and 1/10,000 and 0 methylated/unmethylated CDKN2A alleles (IVD/NL). This indicates the successful detection of methylation with as little as 15 pg of methylated DNA (∼5 genomic equivalents) in 150 ng of excess unmethylated DNA.