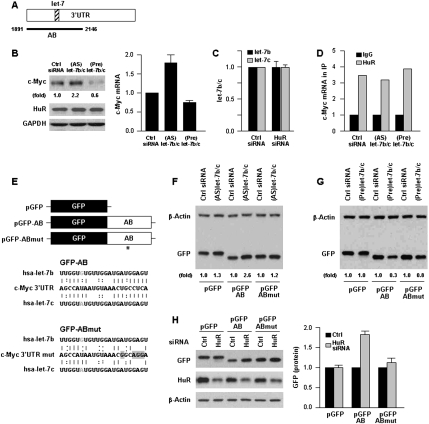
Figure 2.
let-7b/c inhibits c-Myc expression in an HuR-dependent fashion. (A) Schematic of the let-7 interaction site on the c-Myc 3′UTR (hatched). (B) Forty-eight hours after transfection of (AS)let-7b/c or (Pre)let-7b/c, the levels of c-Myc, HuR, and loading control GAPDH (left) were tested by Western blot analysis, and the levels of c-Myc mRNA (right) were measured by RT–qPCR. (C) Forty-eight hours after transfection of Ctrl or HuR siRNAs, the levels of let-7b and let-7c were measured by RT–qPCR analysis. (D) In cells transfected as described in B, the interaction of HuR with c-Myc mRNA was measured by RNP IP followed by RT–qPCR analysis. (E) To test the influence of let-7b/c on c-Myc expression, GFP reporters were prepared in which GFP was linked to the AB segment containing the intact let-7 site (GFP-AB) or a mutant let-7 site (GFP-ABmut) with four point mutations (*) in the seed region that disrupted the interaction of let-7b and let-7c with the c-Myc mRNA (gray highlight). (F,G) Thirty-six hours after transfection of Ctrl siRNA or (AS)let-7b/c (F) or (Pre)let/7b/c (G), plasmid pGFP, pGFP-AB or pGFP-ABmut were transfected and the levels of GFP and loading control β-actin tested 24 h later by Western blot analysis. (H) Following transfection of Ctrl or HuR siRNAs together with plasmids pGFP, pGFP-AB or pGFP-ABmut as explained in F and G, the levels of GFP, HuR, and β-actin were assessed by Western blot analysis (left) and quantified (right). Values in B, C, and H are the means ± SD from three independent experiments. Western blotting data are representative of three or more experiments. Where indicated, “(fold),” and in H, c-Myc or GFP Western blotting signals were quantified by densitometry.