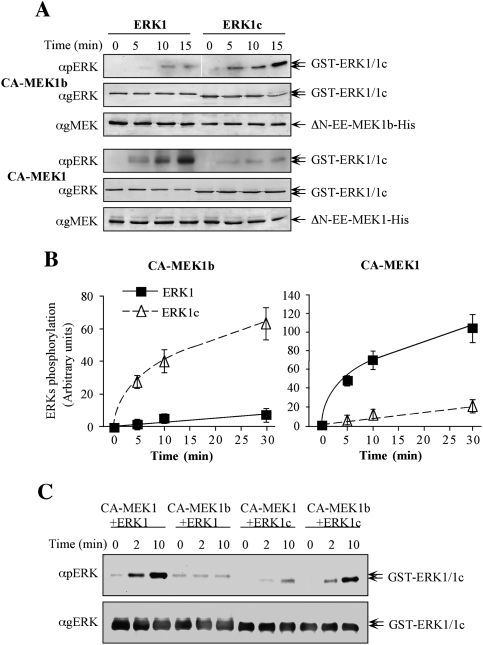
Figure 2.
Specificity studies using constitutively active MEK1b and MEK1. (A) Time course of ERK1 and ERK1c phosphorylation by constitutively active MEK1b and MEK1. In vitro phosphorylation was preformed as described under Materials and Methods with recombinant His-ΔN-EE-MEK1b and His-ΔN-EE-MEK1 as kinases and GST-ERK1 and GST-ERK1c as substrates. The amounts of ERK1/1c and their phosphorylation levels were determined by Western blotting with anti-pERK, anti-gERK(CRS), and anti-gMEK(C-18) Abs. (B) Quantification of ERK1/1c phosphorylation. Known amounts of phosphorylated ERK were added to the blots to form a calibration curve, which enabled the determination of ERK1/1c phosphorylation levels (see text for details). The results in the graphs represent means ± SE of three experiments. (Squares) ERK1 phosphorylation; (triangles) ERK1c phosphorylation. (C) Side-by-side kinetics of ERK1/1c dual phosphorylation by MEK1/1b. In vitro phosphorylation was performed using amounts of recombinant proteins that were found optimal for each phosphorylation [His-ΔN-EE-MEK1 (CA-MEK1), 0.5 μg per reaction; His-ΔN-EE-MEK1b (CA-MEK1b), 0.75 μg; GST-ERK1, 0.5 μg or GST-ERK1c 0.5 μg] for 0, 2, and 10 min at 30°C as described in the Materials and Methods. The levels of ERK1/1c phosphorylation were detected by resolving the samples by one SDS-PAGE and Western blotting using anti-pERK, and anti-gERK(CRS) Abs.