Figure 3.
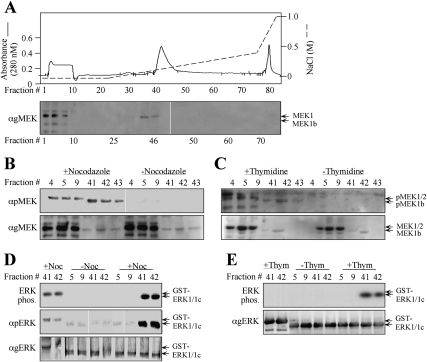
Fractionation of endogenous MEK1b verifies its specificity toward ERK1c. (A) Fractionation of MEK1b on a Mono-Q FPLC column. HeLa cells (10 plates of 10 cm) were treated with nocodazole (100 ng/mL, 24 h) and harvested in Buffer A. Cell extracts were loaded onto a Mono-Q FPLC column, which was washed with Buffer A and developed using an increasing NaCl gradient (dashed line), to give rise to the protein profile shown by the solid line. Aliquots (40 μL, boiled in sample buffer) of every third fraction were subjected to Western blotting with anti-gMEK(H-8) Abs. Identical fractionation of MEK1/2 and MEK1b was observed with extracts from HeLa cells that were harvested 9 h after release from double-thymidine block and from untreated cells (data not shown). (B,C) Endogenous MEK1b from G2/M cells is phosphorylated on its regulatory residues. Fractions containing MEK1/2 (#4, #5, #9) or MEK1b (#41, #42, #43) from cells that underwent treatment with nocodazole as described above (B), 9 h after release from double-thymidine block as described above (C), or untreated cells (B,C, indicated fractions) were subjected to Western blotting with anti-pMEK (top panel) and anti-gMEK(H-8) Ab (bottom panel). Similar results were obtained with Ab from other companies (data not shown). (D,E) The endogenous activated MEK1b from G2/M cells phosphorylates mainly ERK1c in vitro. The indicated aliquots of MEK1/2- or MEK1b-containing fractions from nocodazole-treated cells (D), from cells that were released from double-thymidine block (E), or from untreated cells (E,D, indicated fractions) were used to phosphorylate GST-ERK1c (0.5 μg) or GST-ERK1 (0.5 μg), as described in Material and Methods. The phosphorylated proteins were analyzed by autoradiography (top panels) or by Western blotting with anti-pERK and anti-gERK(CRS) Abs (bottom panels) as indicated.