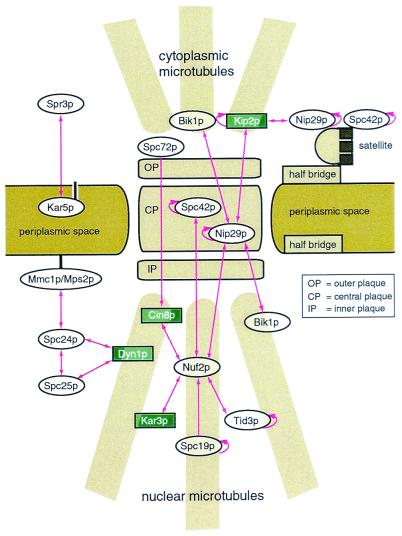
Figure 4.
A schematic representation of interacting SPB components. The trilaminar SPB is shown embedded in the nuclear envelope. (Top) Cytoplasmic microtubules; (Bottom) nuclear microtubules. The half-bridge and satellite structures are depicted to the right of the SPB: both participate in SPB duplication. SPB components that interact via putative coiled coils in this screen are also shown. Protein localization is based on prior immunoelectron microscopy and immunofluorescence studies (8, 30, 46, 48, 56–58). Dyn1p is known to localize to the SPB and to cytoplasmic microtubules (59). As Dyn1p independently contacts two nuclear SPB components in this study, we have also positioned it in the nucleus. For clarity, multiple coiled-coil domains from single proteins have been omitted. Arrowheads point toward DNA-binding domain proteins. Double arrowheads indicate reciprocal interactions. Circular arrows indicate homotypic interactions. The numerous interactions depicted in this figure show how coiled coils may organize the SPB. Interactions between motor proteins (in green) and the SPB provide clues about how the SPB moves and is moved by microtubules.