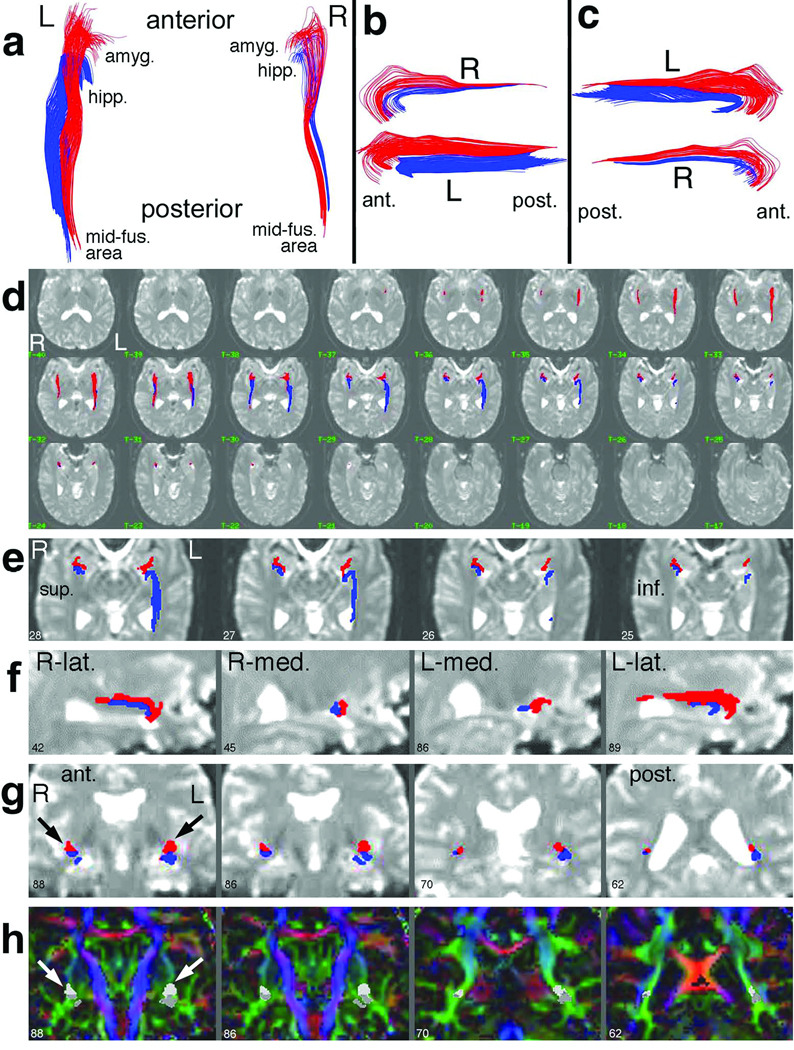
Figure 2.
Typical pathway results for one subject. In (a–c), the amygdalo-fusiform (red) and hippocampo-fusiform (blue) pathways are shown in 3D projection display, viewed from above (a), from the left side (b), and from the right side (c). The views in (b,c) are slightly obliqued (viewing superior-to-inferior by 20°) to better demonstrate the separation at the medial temporal lobe (see anterior parts of b,c). A 2D anatomical overlay of the pathways onto contiguous transverse 1.25-mm I0 images (d) documents the precise anatomical location. In (e), a close-up display of four consecutive slices in (d) shows the pathway terminations in relationship to amygdala and hippocampus. Select sagittal (f) and coronal (g) reformatted images demonstrate the relationship of the pathways to various anatomical structures. Finally, pathways are overlayed onto coronal color-direction images (h), calculated as in (62), to demonstrate the location of the pathways with respect to various white matter structures. The same slices are displayed in (g) and (h), with the red/blue pathways in (g) respectively shown as light/dark gray in (h) (see arrows). In all figures, the image numbers correspond to the sequential number of 1.25-mm sections. Abbreviations: L = left, R = right; ant. = anterior; post. = posterior; sup. = superior; inf. = inferior; lat. = lateral; med. = medial; amyg. = amygdala; hipp. = hippocampus; mid-fus. = mid-fusiform.