Figure 1.
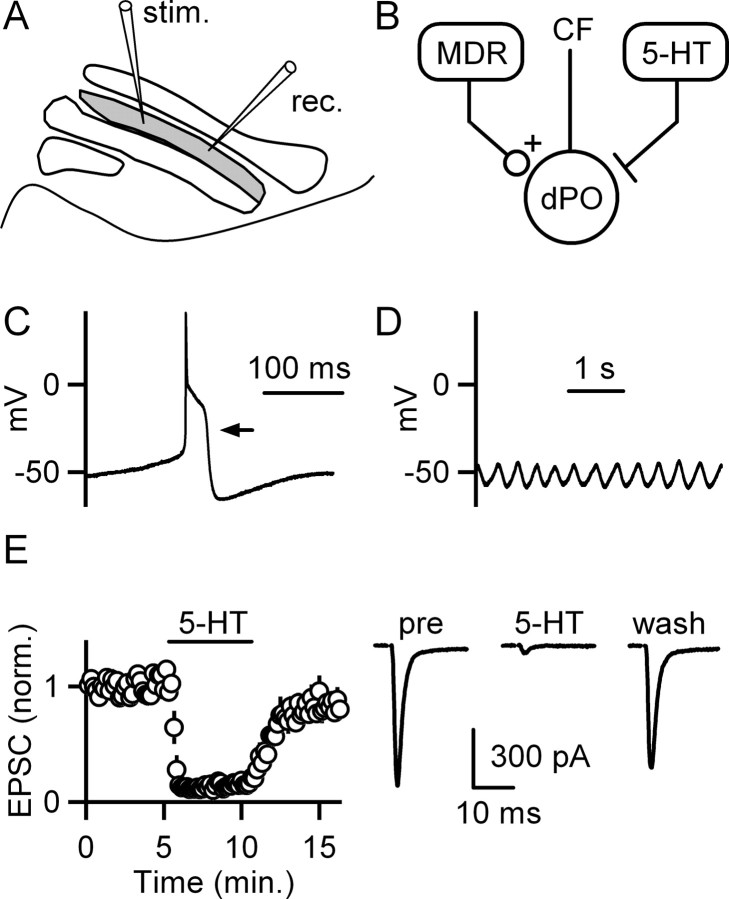
Excitatory synapses onto inferior olive neurons are suppressed by serotonin. A, A schematic of the slice preparation illustrates recording (rec.) and stimulation (stim.) sites within the dPO (gray) of the IO. B, A simplified circuit shows that neurons in MDRs provide excitatory synapses to neurons in the dPO. Brainstem nuclei provide a strong serotonergic (5-HT) input to the IO. Cells in the IO provide climbing fiber (CF) synapses whose primary target is Purkinje cells in the cerebellar cortex. C, Example recordings from dPO cells using a potassium-based pipette solution show a spontaneous action potential (C) and spontaneous subthreshold membrane potential oscillations (D). E, The effects of bath-applied 5-HT (10 μm) on EPSCs are illustrated by the time courses of EPSC amplitudes (left; n = 5 cells; means ± SEM) and by example traces from a representative experiment (right).