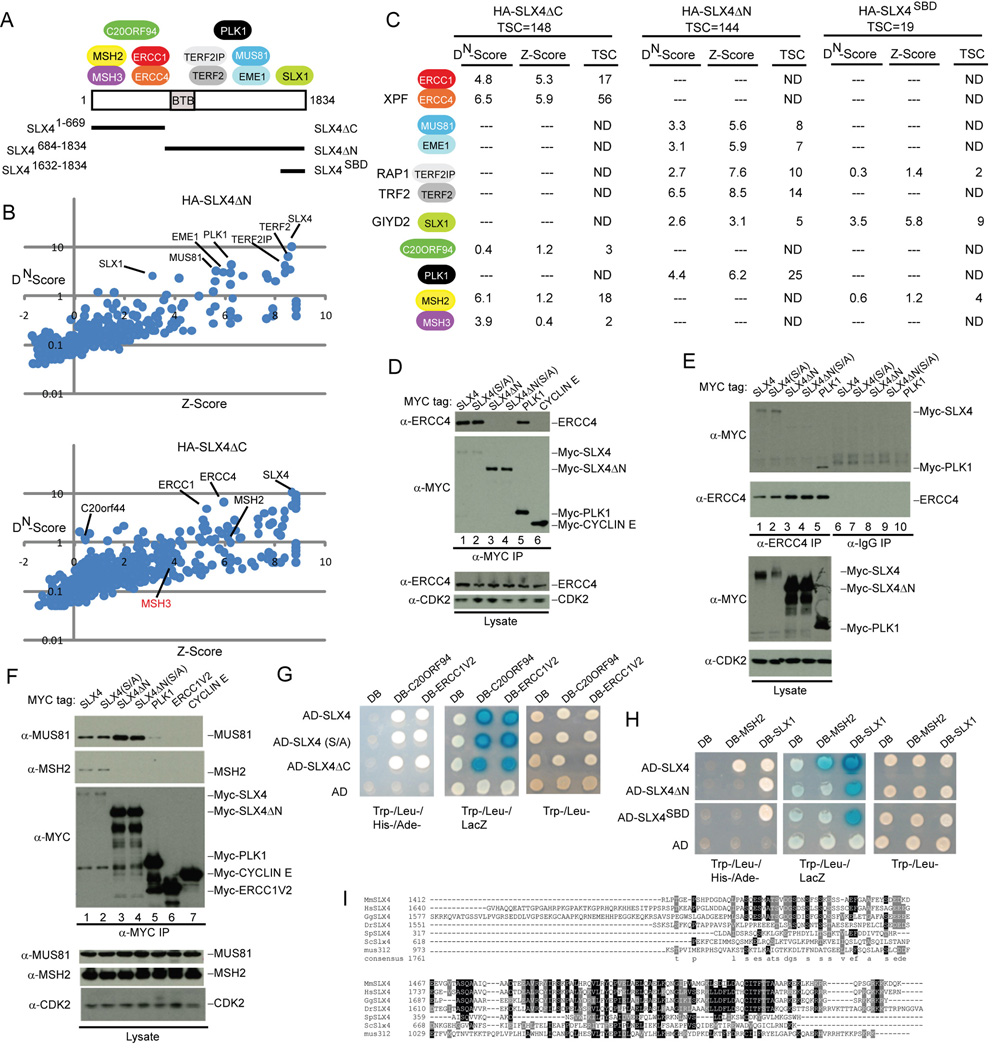
Figure 2. Structural anatomy of the human SLX4 complex.
(A) Summary of the interaction data showing the approximate location of binding between SLX4 and associated proteins.
(B) DN-Score versus Z-Score plots for HA-SLX4ΔN and HA-SLX4ΔC showing the identity of proteins identified by mass spectrometry (see Figure 1 legend for details).
(C) Summary of proteomic data for HA-SLX4ΔN, HA-SLX4ΔC, and HA-SLX4SBD. TSC, total spectral counts. The full list of interacting proteins is provided in Table S1.
(D–F) Domain mapping of SLX4 and its associated proteins. The indicated MYC-tagged proteins were expressed in 293T cells, immunoprecpitated as indicated, and immunoblotted. α-CDK2; loading control.
(G, H) Interaction of SLX4 with target proteins using the yeast two-hybrid system. The indicated proteins were cloned into activation domain (AD) or DNA-binding domain (DB) vectors and two-hybrid analysis performed as described under Experimental Procedures.
(I) Sequence relationship between vertebrate, yeast, Drosophila and C. elegans SLX4 in the C-terminal region involved in binding SLX1.