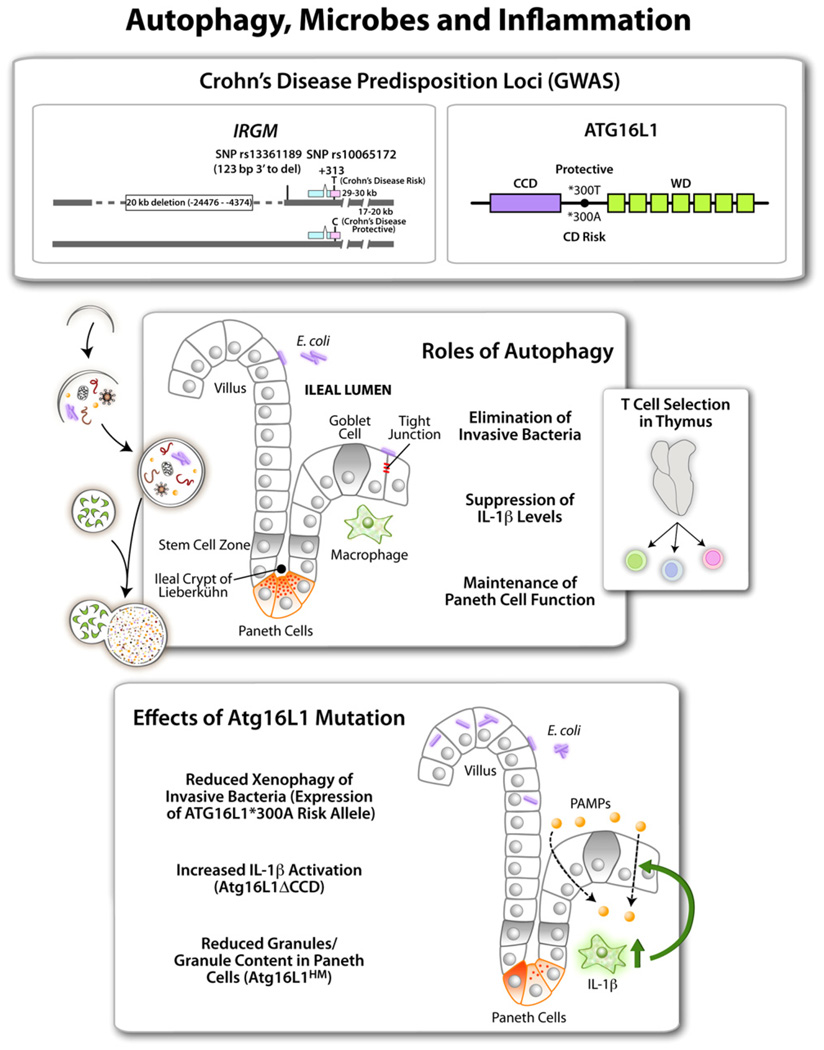
Figure 2. Autophagy in Inflammation.
Top shows two autophagy factors identified as Crohn’s disease (a form of inflammatory bowel disease) susceptibility loci. The IRGM gene has single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNP)and a 20 kb deletion in the promoter region associated with CD. ATG16L1 alleles encode either a protective ATG16L1*300T or a risk form of ATG16L1*300A (CCD, coiled coil domain; green boxes, WD repeats domain [absent in yeast Atg16]). Middle panel shows intestinal epithelium with different cell types along with the proposed functions of autophagy in the ileal epithelium. Side box shows that thymic selection of naive T cell repertoires depends on autophagy, and autophagic anomalies may contribute to inflammation at peripheral sites such as intestinal mucosa. Bottom box lists 3 different effects reported for Atg16L1 (mouse) or ATG16L1 (human epithelial cells) mutations. ATG16L1*300A has been tested in cell lines. Atg16L1HM, hypomorphic Atg16L1 allele, and Atg16LΔCCD construct have been tested in vivo in transgenic mice.