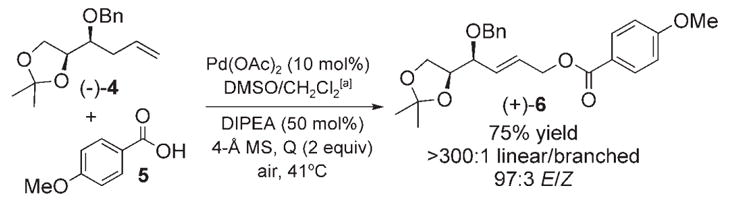
Table 1.
Investigation into the linear allylic oxidation reaction to form the hexose precursor 6.
 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Entry | DMSO/CH2Cl2 Molarity [M] | Quinone (Q) | Acid 5 (equiv) | Yield [%][c] |
| 1 | 0.33 | BQ | 15 | 23[d] |
| 2 | 0.33 | BQ | 15 | 45 |
| 3 | 0.33 | PhBQ | 15 | 55 |
| 4 | 0.6 | PhBQ | 10 | 66 |
| 5 | 1.0 | PhBQ | 5 | 67 |
| 6[b] | 2.0 | PhBQ | 3 | 75 |
| 7[b] | 2.0 | PhBQ | 3 | 71[e] |
| 8 | 2.0 | PhBQ | 3 | 63[f] |
| 9 | 3.0 | PhBQ | 1.5 | 50 |
DMSO/CH2Cl2 (3.2:1).
Linear to branched allylic ester and E/Z ratios were determined by HPLC for the material obtained from entries 6 and 7 on comparison with branched or acetonide-free E and Z standard compounds: linear/branched >300:1, E/Z =30:1 and 36:1 (for entries 6 and 7, respectively).
Yield of isolated product from the reactions carried out on a 1 mmol scale (4, 262 mg). Yields and selectivities represent an average of at least 2 runs.
With no DIPEA added.
[Pd(CH3CN)4](BF4)2 (10 mol%), 13% of 4 was recovered.
Pd(OAc)2 (5 mol%). Bn =benzyl, DIPEA=N,N-diisopropylethylamine, MS =molecular sieves.
