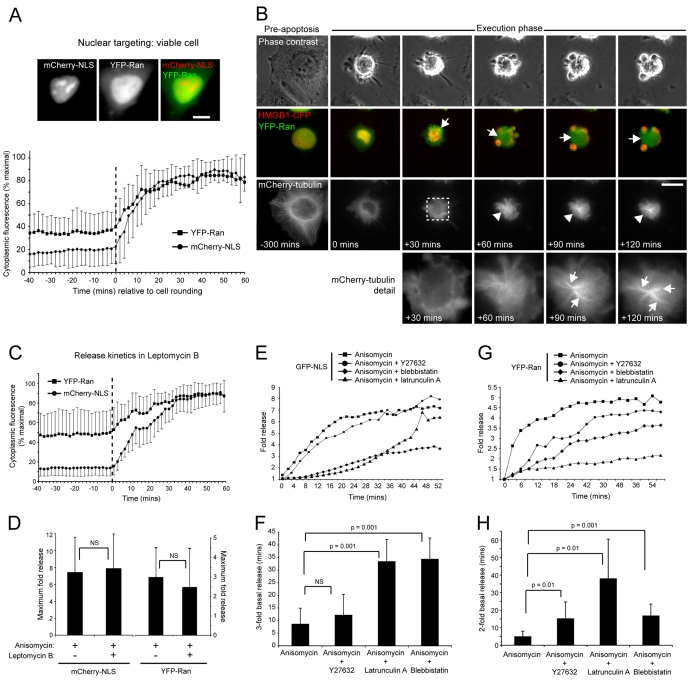
Fig. 2.
Temporal and kinetic aspects of apoptotic nuclear Ran release. (A) Quantitation of cytoplasmic fluorescence intensities of mCherry-NLS and YFP-Ran (mean±s.d.), expressed as a percentage of maximum obtained up to 60 minutes post-cell rounding (initiation of rounding is normalised to 0 minutes and is indicated by the hatched vertical line). Example images of a co-transfected viable cell are shown at the top. (B) Nuclear Ran release occurs as a prelude to apoptotic microtubule assembly. HeLa cells transiently co-expressing mCherry-tubulin, YFP-Ran and HMGB1-CFP induced into apoptosis by anisomycin treatment, and imaged by time-lapse microscopy. Nuclear YFP-Ran release was visualised within the first ∼25 minutes of apoptotic execution, and the YFP-Ran-enriched apoptotic cytoplasm (arrows) supported the assembly of bundled microtubule arrays (arrowheads). This image sequence was obtained from supplementary material Movie 3, and zoom panels are shown at the bottom. (C,D) Effect of leptomycin B on apoptotic nuclear release. (C) Release kinetics in HeLa cells transiently co-expressing YFP-Ran and mCherry-NLS, induced into apoptosis by anisomycin in the presence of Leptomycin B (mean±s.d.) (initiation of rounding is normalised to 0 minutes and is indicated by the hatched vertical line). (D) Comparison of the maximal apoptotic cytoplasmic fluorescence intensity increase of mCherry-NLS and YFP-Ran in the absence or presence of leptomycin B (mean+s.d.). (E-H) Actin–myosin-II inhibition delays apoptotic nuclear release. (E,G) Kinetics of GFP-NLS (E) and YFP-Ran (G) release in HeLa cells treated with anisomycin in the absence or presence of Y27632, latrunculin A or blebbistatin. Standard deviations are omitted to improve clarity. (F,H) Time taken for a threefold increase in cytoplasmic GFP-NLS fluorescence (F) and a doubling in cytoplasmic YFP-Ran release (H) in the absence or presence of Y27632, latrunculin A or blebbistatin (mean+s.d.). Bars, 10 μm.