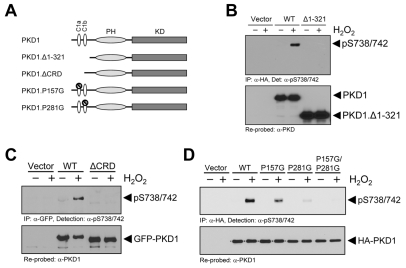
Fig. 3.
Functional N-terminal and C1 domains in PKD1 are required for its activation by oxidative stress. (A) Overview PKD1 structure and mutants. PKD1 consists of two C1 domains, C1a and C1b (CRD domain), a pleckstrin homology domain (PH) and a kinase domain (KD). PKD1 deletion and point mutants were generated to examine the importance of DAG binding on PKD1 activation in response to oxidative stress. PKD1.Δ1-321: PKD1 mutant with deletion of the first 321 amino acids of the N-terminal domain. PKD1.ΔCRD: PKD1 mutant with deletion of the region comprising C1a and C1b (CRD domain). PKD1.P157G: PKD1 point mutant with a P to G mutation that blocks DAG binding by the C1a domain, but leaves the tertiary structure of PKD1 intact. PKD1.P281G: PKD1 point mutant with a P to G mutation that blocks DAG binding by the C1b domain. (B) HeLa cells were transfected with vector control, wild-type PKD1 or PKD1.Δ1-321. Cells were stimulated with H2O2 (10 mM, 10 minutes) as indicated. PKD1 was immunoprecipitated (α-HA) and resolved by SDS-PAGE. Western blotting was performed with α-pS738/S742. Total PKD1 was detected by stripping and re-probing for PKD1. (C) HeLa cells were transfected with vector control, wild-type PKD1 or PKD1.ΔCRD. Cells were stimulated with H2O2 (10 mM, 10 minutes) as indicated. PKD1 was immunoprecipitated (α-HA) and resolved by SDS-PAGE. Western blotting was performed with α-pS738/S742. Total PKD1 was detected by stripping and re-probing for PKD1. (D) HeLa cells were transfected with vector control, wild-type PKD1, PKD1.P157G, PKD1.P281G or PKD1.P157G.P281G. Cells were stimulated with H2O2 (10 mM, 10 minutes) as indicated. PKD1 was immunoprecipitated (α-HA) and resolved by SDS-PAGE. Western blotting was performed with α-pS738/S742. Total PKD1 was detected by stripping and re-probing for PKD1. All experiments were performed at least three times and obtained similar results.