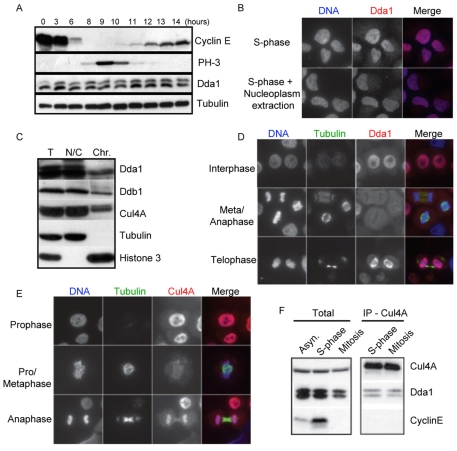
Fig. 4.
Dda1 associates with the chromatin in a cell cycle-dependent manner. (A) Cells were arrested in S-phase using a double thymidine block and samples were collected at various times after release. Protein extracts were separated by SDS-PAGE and immunoblotted with antibodies directed against Dda1 and the indicated cell cycle markers (Cyclin E and PH3). Tubulin was used as a loading control. (B) The localization of Dda1 was analyzed by immunofluorescence in interphase cells pre-extracted (left panels) or not (right panels) with buffers that remove nucleoplasmatic proteins. DAPI staining was used to visualize the DNA. Merge images are shown in the right row. (C) Total lysates (T) were prepared from aphidicolin-arrested S-phase cells and separated into a nucleo-cytoplasmic (NC) and a chromatin-bound fraction (Chr), solubilized after digestion with micrococcal nuclease. Fractions were separated by SDS-PAGE and immunoblotted with antibodies directed against Dda1, Ddb1, Cul4A, tubulin and histone H3. (D,E) Dda1 and Cul4A localize to the nucleus but Dda1 is excluded from chromatin in mitosis. The localization of Dda1 (panel D) and Cul4A (panel E) was analyzed by immunofluorescence at different stages of mitosis. Antibodies against tubulin visualize the mitotic spindle, and the DNA was stained with DAPI (left row). Merge images are presented in the right row. Note that Cul4A remains associated with chromosomes throughout mitosis, whereas Dda1 staining is diffuse in metaphase and anaphase cells. (F) Cul4A immunoprecipitates from extracts prepared from cells arrested in S-phase or mitosis with aphidicolin or nocodazole, respectively, were analyzed by immunoblotting for the presence of Cul4A, Ddb1 and Dda1 as indicated.