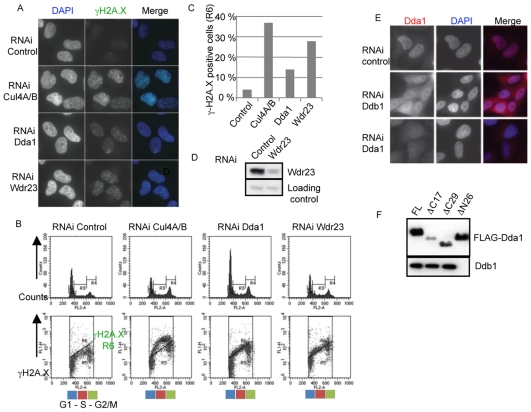
Fig. 5.
Dda1 functionally interacts with a subset of CRL4s. (A) Cul4A- and B-, Dda1- and Wdr23-depleted cells accumulate γH2A.X foci. Cells were immunostained with anti-phospho H2A.X antibodies and DNA was counterstained with DAPI. (B,C) Quantification of the number of γH2A.X-positive cells by FACS analysis in control cells or cells depleted of Cul4A and B, Dda1 and Wdr23. Cells were fixed with ethanol, stained with an γH2A.X antibody and analyzed by FACS. The number of γH2A.X-positive cells (R6 area) was plotted. (D) Immunoblotting of Wdr23 in extracts prepared from control and Wdr23 siRNA-depleted HeLa cells. (E) Ddb1 is required for nuclear accumulation of Dda1. Endogenous Dda1 was localized by indirect immunofluorescence (left column) in control cells (upper panel), or cells treated with Ddb1 (middle panel) or Dda1 siRNA (bottom panel). DNA was counterstained with DAPI (middle column), and merged images are presented in the right panels. (F) Dda1 uses its N-terminal domain to bind Ddb1. Full-length and truncated versions of FLAG-Dda1 that remove the first 26 amino acids (ΔN26), or the last 17 and 29 amino acids, respectively (ΔC17 and ΔC29), were transiently expressed in HEK 293T and immunoprecipitated with M2-agarose. The immunoprecipitates were separated by SDS-PAGE and blotted with specific Ddb1 (upper panel) and FLAG antibodies (lower panel).